The importance of internal controls has become center stage for companies seeking to scale, reduce risk, and meet growing demands. Internal controls form the infrastructure that supports financial accuracy, operational integrity, and strategic decision-making.

Compelling data underscore the urgency of implementing strong internal controls. In FY 2024, CFO Act agencies within the U.S. federal government reported 53 material weaknesses in financial reporting controls, a reminder that even the most prominent institutions are vulnerable without proper oversight.
What are Internal Controls?
Internal controls are essential mechanisms that ensure the integrity and accuracy of financial reporting, compliance, and efficient operation. These controls are not merely procedures but are integral to an organization’s framework, safeguarding assets and enhancing the reliability of financial statements.
Definition and Purpose of Internal Controls
Internal controls encompass a set of policies and procedures implemented by an organization’s management and board of directors to achieve objectives related to operational efficiency, reliable financial reporting, and compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
They defend against errors and fraud, ensuring business processes operate as intended. The primary purposes of internal controls include:
- Operational Efficiency: Ensuring that business operations are practical and efficient.
- Reliable Financial Reporting: Providing accurate and timely financial information to stakeholders.
- Compliance: Adhering to laws, regulations, and internal policies.
Key Components of an Effective Internal Control System
Transitioning from the definition, it’s crucial to understand the foundational elements that constitute an effective internal control system. The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) outlines five interrelated components:
- Control Environment: This sets the organization’s tone, influencing its people’s control consciousness. It includes the integrity, ethical values, and competence of the organization’s people.
- Risk Assessment: The entity identifies and analyzes relevant risks to achieving its objectives, forming a basis for determining how risks should be managed.
- Control Activities: The policies and procedures that help ensure management directives are carried out. These include approvals, authorizations, verifications, reconciliations, and segregation of duties.
- Information and Communication: Systems or processes that support identifying, capturing, and exchanging information in a form and time frame that enable people to carry out their responsibilities.
- Monitoring: Processes used to assess the quality of internal control performance over time, including regular management and supervisory activities, and separate evaluations.
How Internal Controls Support Financial Accuracy
Building upon the components, internal controls are pivotal in maintaining financial accuracy. They ensure that monetary transactions are recorded correctly, financial statements are prepared accurately, and financial reporting is reliable.
Key ways internal controls support financial accuracy include:
- Transaction Authorization: Ensuring that all transactions are authorized by appropriate personnel before execution.
- Segregation of Duties: Dividing responsibilities among individuals to reduce the risk of error or inappropriate actions.
- Reconciliations: Regularly comparing data from different sources to identify and correct discrepancies.
- Access Controls: Restricting access to financial systems and data to authorized personnel only.
Moreover, a study found that 42% of fraud in small businesses was due to a lack of internal controls. This statistic underscores the critical role internal controls play in preventing fraud and ensuring the accuracy of financial information.
The Role of Internal Controls in Fraud Prevention
The importance of internal controls cannot be overstated, especially regarding safeguarding against fraudulent activities. These controls serve as the first line of defense, ensuring financial operations are conducted with integrity and transparency.
Identifying and Preventing Financial Fraud
Fraudulent activities can take various forms, from embezzlement to financial statement manipulation. Implementing robust internal controls in accounting is crucial to detecting and preventing such malpractices.
Moreover, fostering a culture of ethical behavior and accountability within the organization plays a significant role in fraud prevention strategies. When employees understand the repercussions of fraudulent activities and the importance of adhering to established protocols, the likelihood of misconduct diminishes.
How Segregation of Duties Strengthens Internal Controls
Transitioning to another critical aspect, segregation of duties is a fundamental principle in establishing adequate internal controls. By dividing responsibilities among different individuals, organizations can prevent one person from having control over all aspects of a financial transaction, thereby reducing the risk of errors and fraud.
For instance, the person responsible for authorizing payments should not be the same individual who processes them. This separation ensures that any irregularities are more likely to be detected by another party, creating a system of checks and balances.
Implementing segregation of duties requires additional staffing or role restructuring, but the benefits of fraud prevention and operational efficiency are substantial. Organizations should regularly review and adjust these divisions to adapt to changes in operations and personnel.
Implementing Checks and Balances to Reduce Risk
Establishing comprehensive checks and balances, building upon the segregation of duties, is essential for mitigating risks associated with financial operations. These mechanisms involve multiple review and approval processes that ensure accuracy and compliance with established policies.
Key components of adequate checks and balances include:
- Dual Authorization: Requiring two or more individuals to approve significant transactions adds an extra layer of scrutiny.
- Regular Audits: Periodic internal and external audits are conducted to assess internal controls’ effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
- Reconciliation Procedures: Systematically comparing financial records to detect and correct discrepancies promptly.
How Internal Controls Ensure Compliance and Risk Management
The importance of internal controls extends beyond financial accuracy to encompass comprehensive compliance and internal controls frameworks. These systems are vital for organizations to comply with laws and regulations, ensuring operations align with legal standards and ethical practices.
Meeting Regulatory and Compliance Standards
Organizations must establish robust internal controls to meet regulatory requirements and uphold compliance standards. Frameworks like the COSO provide structured approaches to designing and implementing effective control systems.
These frameworks emphasize the need for a control environment that promotes integrity and ethical values, risk assessment processes to identify and analyze potential compliance risks, and control activities that enforce policies and procedures.
One critical aspect of compliance is adhering to SOX, particularly Section 404, which mandates management and external auditors to report on the adequacy of a company’s internal control over financial reporting. This requirement ensures that companies maintain transparency and accountability in their financial disclosures.
Moreover, internal controls facilitate compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards, such as the FFMIA for federal agencies. These controls help maintain accurate records, safeguard assets, and ensure operations follow applicable laws and regulations.
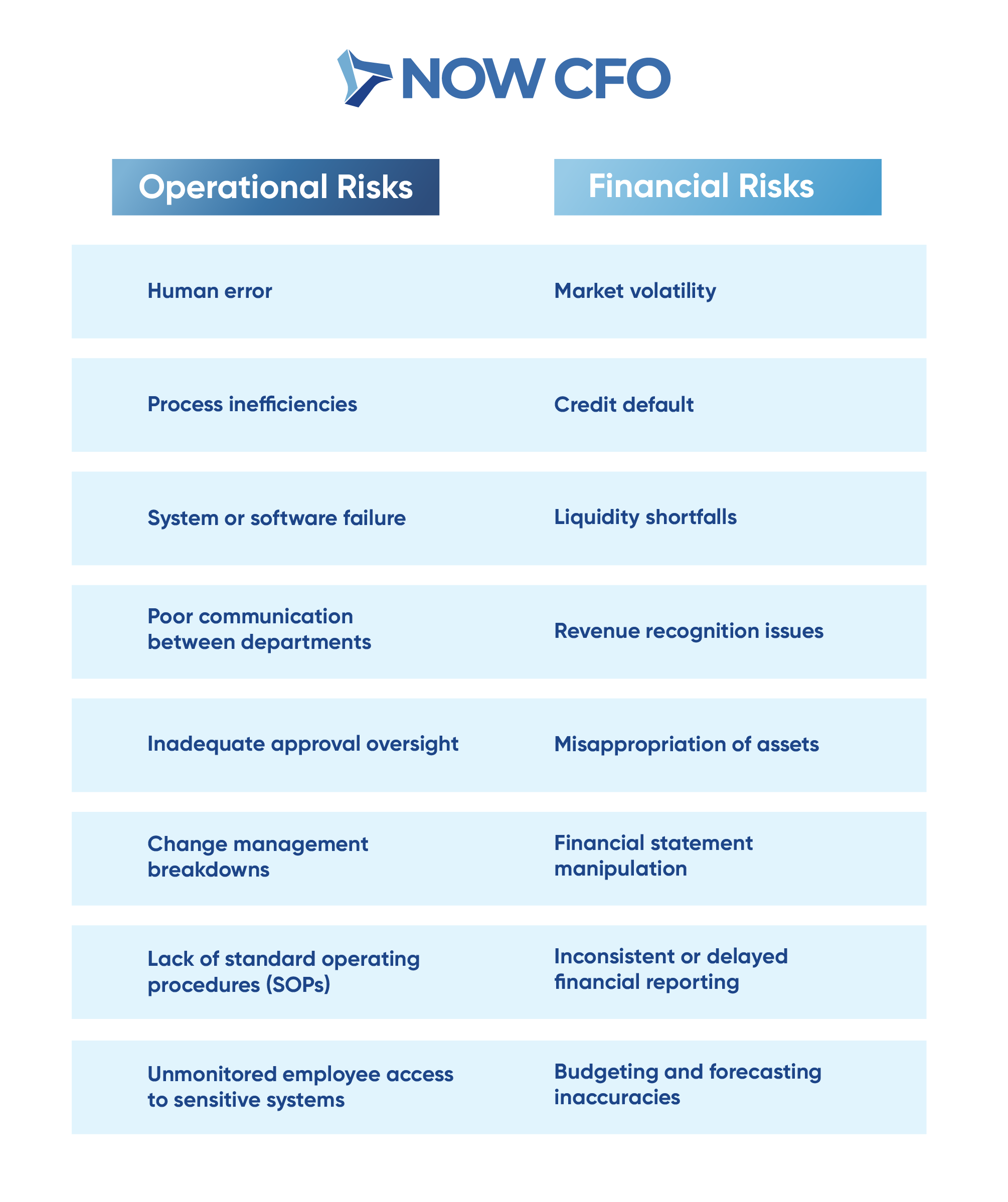
Reducing Operational and Financial Risks
Beyond regulatory compliance, internal controls are pivotal in mitigating operational and financial risks. Organizations can safeguard against disruptions that may impact their objectives by identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing preventive measures.
The following table outlines common operational and financial risks along with corresponding internal control measures:
The Role of Internal Audits in Strengthening Compliance
Internal audits are critical to evaluating and enhancing the effectiveness of internal controls. They provide independent assessments of an organization’s control environment, identifying areas for improvement and ensuring that controls are functioning as intended.
Internal audit best practices include:
- Evaluating Control Effectiveness: Assessing whether existing controls adequately address identified risks and comply with regulatory requirements.
- Identifying Control Gaps: Detecting deficiencies or weaknesses in control processes that may expose the organization to risks.
- Recommending Improvements: Providing actionable suggestions to enhance control mechanisms and mitigate identified risks.
- Monitoring Compliance: Ensuring the organization adheres to internal policies and external regulations through continuous oversight.
Best Practices for Developing Strong Internal Controls
Developing a robust internal control system is essential for organizations aiming to ensure financial integrity, compliance, and operational efficiency. Implementing best practices in establishing policies, leveraging technology, and conducting regular reviews fortifies the organization’s defense against errors and fraud.
Establishing Clear Policies and Procedures
The development of comprehensive policies and procedures is a foundational step in strengthening internal controls. These guidelines serve as a roadmap for employees, delineating responsibilities and standardizing processes.
Key elements to consider include:
- Documentation: Clearly outline procedures for financial transactions, approvals, and reporting.
- Role Definition: Specify duties and responsibilities to prevent overlap and ensure accountability.
- Approval Hierarchies: Establish authorization levels for various transactions to maintain control over financial activities.
- Training Programs: Implement regular training sessions to ensure staff know policies and their roles in maintaining controls.
Leveraging Technology to Enhance Internal Control Systems
Integrating technology into internal control systems significantly enhances their effectiveness and efficiency. Automation reduces the likelihood of human error and allows for real-time monitoring of financial activities.
Consider the following technological implementations:
- ERP Systems: Centralize data and streamline processes, providing a unified platform for financial management.
- Automated Reconciliation Tools: Facilitate the comparison of financial records, quickly identifying discrepancies.
- Access Controls: Utilize software to manage user permissions, ensuring that only authorized personnel can perform specific tasks.
- Audit Trail Software: Maintain records of all transactions and changes, aiding in detecting and investigating irregularities.
Conducting Regular Internal Control Reviews and Audits
Regular reviews and audits are critical in assessing the effectiveness of internal controls and identifying areas for improvement. These evaluations help organizations comply with regulations and adapt to changes in the business environment.
Internal audits should focus on:
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate potential risks and the adequacy of controls to mitigate them.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure operations adhere to internal policies and external regulations.
- Process Improvement: Identify inefficiencies and recommend enhancements to procedures and controls.
Common Internal Control Weaknesses and How to Address Them
Even well-structured organizations can encounter vulnerabilities within their internal control systems. Recognizing and addressing these weaknesses is crucial to maintaining financial integrity and operational efficiency.
Recognizing Gaps in Financial Oversight
A significant weakness in internal controls is the lack of adequate financial oversight. This can manifest as inadequate supervision of financial transactions, insufficient review of financial statements, or the absence of regular audits. Such gaps can lead to unnoticed errors and increase the risk of fraud.
For instance, when management fails to review financial reports or reconcile accounts regularly, discrepancies may persist, leading to inaccurate financial reporting. Additionally, the absence of a robust audit trail can make it challenging to trace transactions, hindering the detection of irregularities.
Strengthening Internal Reporting and Documentation
Another prevalent weakness is the lack of comprehensive internal reporting and documentation. Without detailed records, organizations struggle to track transactions, justify financial decisions, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Documentation serves as evidence of compliance and provides a clear audit trail. It enables organizations to monitor financial activities, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Moreover, well-maintained records facilitate smoother audits and reduce the risk of penalties due to non-compliance.
To enhance internal reporting and documentation:
- Standard Reporting Procedures: Develop templates and guidelines to ensure consistency across all departments.
- Implement Document Management Systems: Utilize technology to store, organize, and retrieve documents efficiently.
- Regularly Update Records: Ensure all financial documents are current and accurately reflect transactions.
- Train Staff: Educate employees on the importance of documentation and the correct procedures to follow.
Improving Employee Training on Internal Control Protocols
Building upon documentation, the effectiveness of internal controls heavily relies on employee awareness and adherence to established protocols. Without proper training, even the most robust control systems can fail due to human error or negligence.
To bolster employee understanding and compliance:
- Develop Comprehensive Training Programs: Design courses that cover all aspects of internal controls relevant to each role.
- Conduct Regular Workshops and Seminars: Keep staff updated on any changes in procedures or regulations.
- Utilize Real-World Scenarios: Incorporate case studies to illustrate the consequences of weak internal controls.
- Assess Understanding: Implement quizzes or assessments to gauge employee comprehension and identify areas needing reinforcement.
- Encourage Open Communication: Create channels for employees to ask questions and report concerns regarding internal controls.
How an Outsourced CFO Can Help Strengthen Internal Controls
As organizations strive for financial integrity and compliance, leveraging the expertise of an outsourced CFO becomes a strategic move. These professionals bring specialized knowledge and objective perspectives, enhancing the organization’s ability to manage risks and adhere to regulatory standards.

Providing Expertise in Risk Assessment and Compliance
Outsourced CFOs offer invaluable insights and strategies to fortify internal controls. Their contributions include:
- Comprehensive Risk Evaluation: Identifying potential financial and operational risks that could impact the organization’s objectives.
- Regulatory Compliance Guidance: Ensuring adherence to laws and regulations, such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, to maintain transparency and avoid penalties.
- Internal Control Enhancement: Developing and implementing robust control systems to detect and prevent errors or fraud.
- Policy and Procedure Development: Establishing clear guidelines to standardize processes and promote accountability.
Enhancing Financial Oversight with External Review
Building upon risk assessment, outsourced CFOs provide an external perspective crucial for unbiased financial oversight. Their independent evaluations help identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement that internal teams might overlook.
For instance, an outsourced CFO can conduct thorough reviews of financial statements, ensuring accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. They also facilitate audits by preparing necessary documentation, addressing auditor inquiries, and streamlining the audit process.
Moreover, their experience across various industries equips them with the best practices that can be tailored to the organization’s specific needs. This cross-industry knowledge enhances the organization’s financial strategies and internal controls.
Implementing Scalable Internal Control Frameworks
As organizations grow, efficient internal control systems must evolve to accommodate increased complexity. Outsourced CFOs assist in designing scalable frameworks that adapt to the organization’s changing needs.
Key components of scalable internal control frameworks include:
- Modular Control Structures: Developing controls that can be expanded or modified as the organization grows.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing software solutions to automate control processes, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implementing systems to assess the effectiveness of controls and make necessary adjustments regularly.
- Training and Development: Educating staff on control procedures to ensure consistent organizational application.
How NOW CFO Can Help
NOW CFO specializes in providing outsourced CFO services tailored to enhance internal controls. Our team of experts offers:
- Customized Risk Management Strategies: Assessing and developing targeted operations and financial risk management plans.
- Compliance Support: Guiding organizations through regulatory requirements to ensure full compliance.
- Internal Control Development: Designing and implementing control systems that align with the organization’s objectives and growth plans.
- Ongoing Oversight: Providing continuous support to monitor and refine internal controls as the organization evolves.
Conclusion: Strengthening Your Business with Internal Controls
When done right, internal controls do more than help organizations pass the audit; they create the foundation for growth. The importance of internal controls lies in their ability to empower leadership with accurate insights, prevent costly mistakes, and safeguard stakeholder trust.
If you’re unsure where to start or how your current controls stack up, NOW CFO is here to help. Our outsourced CFOs offer the deep financial expertise needed to assess risk, close control gaps, and design scalable, audit-ready frameworks tailored to your business.
Whether you’re looking to optimize current processes, prepare for an audit, or address compliance concerns, we can help you confidently move forward. Schedule a complimentary consultation with our financial experts to answer your questions.














