Quality business accounting is more than just balancing books; it demands a strategic approach to accounting. A staggering 82% of SMEs fail due to poor cash flow management, underscoring the critical need for effective financial oversight.
By integrating both managerial accounting and financial accounting, businesses can achieve a holistic view of their financial health, enabling informed decisions that align with both internal goals and external requirements.
What is Managerial Accounting?
Managerial accounting is an essential internal tool for businesses. It provides detailed financial insights that support strategic planning and operational control.
Definition and Purpose of Managerial Accounting for Business Growth
Managerial accounting involves identifying, measuring, analyzing, and interpreting financial information to assist managers in making informed business decisions. Its primary purpose is to provide internal stakeholders with relevant data that aids in planning, controlling, and evaluating business operations.
Unlike financial accounting, managerial accounting is more flexible and forward-looking. It allows organizations to tailor reports to meet specific internal needs, facilitating more timely and relevant decision-making processes.
For instance, managerial accounting encompasses various functions such as budgeting, forecasting, and performance evaluation. These activities enable managers to set financial goals, monitor progress, and implement corrective actions when necessary.
How Managerial Accounting Helps in Business Decision-Making
Managerial accounting enhances business decision-making by providing detailed financial analyses and insights. These management accounting best practices help you make informed choices.
Key contributions of managerial accounting to decision-making include:
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Developing detailed budgets and financial forecasts helps set financial targets and anticipate future financial conditions.
- Cost Analysis: Analyzing the costs associated with products, services, and operations helps identify areas where efficiencies can be improved. Seattle University
- Performance Evaluation: Assessing the financial performance of departments or projects helps recognize successful strategies and areas needing improvement.
Key Reports Used in Managerial Accounting
Managerial accounting utilizes various reports to provide insights into the financial aspects of business operations. These reports are tailored to meet the specific needs of internal stakeholders and support effective decision-making.
Some of the key reports include:
- Budgets: Detailed plans outlining expected revenues and expenditures, serving as a financial roadmap for the organization.
- Forecasts: Projections of future financial outcomes based on historical data and market trends, aiding in strategic planning.
- Cost Analyses: Evaluations of the costs associated with specific business activities, products, or services, helping to identify opportunities for cost savings.
These reports enable managers to monitor financial performance, control operational costs, and make decisions that drive business success.
What is Financial Accounting?
Financial accounting is a cornerstone of transparent business operations. It offers a structured approach to recording and reporting financial transactions. This discipline ensures that stakeholders have access to accurate and standardized financial information, facilitating informed decision-making.
Definition and Purpose of Financial Accounting for Business Growth
Financial accounting involves systematically recording, summarizing, and reporting a company’s financial transactions over a specific period. The primary objective is to provide external stakeholders with reliable and comparable financial information.
This branch of accounting adheres to standardized frameworks like GAAP or IFRS. These standards ensure consistency and transparency across financial statements, enabling stakeholders to accurately assess a company’s financial health and performance.
Unlike managerial accounting, financial accounting emphasizes historical data and compliance. Its structured approach evaluates a company’s profitability, liquidity, and solvency, serving as a critical tool for external analysis and decision-making.
Importance of Financial Accounting for External Reporting
Financial accounting plays a pivotal role in external reporting by giving stakeholders a clear picture of a company’s financial position. This transparency is essential for building trust and facilitating economic decisions.
Key aspects include:
- Investor Confidence: Accurate financial statements enable investors to assess the viability and profitability of their investments.
- Creditworthiness Assessment: Lenders and creditors rely on financial reports to determine a company’s ability to meet its financial obligations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to reporting standards ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of penalties and legal issues.
Moreover, standardized financial reporting facilitates comparability across companies and industries, aiding stakeholders in benchmarking and strategic planning.
Key Reports Used in Financial Accounting
Financial accounting encompasses several key reports. The role of financial statements in business is to provide a comprehensive view of financial entities:
- Income Statement: Also known as the profit and loss statement, it details revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period and highlights operational efficiency.
- Balance Sheet: This snapshot of a company’s financial position lists assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time, offering insights into financial stability.
- Cash Flow Statement: It tracks the inflow and outflow of cash, categorizing activities into operating, investing, and financing, thereby assessing liquidity and cash management.
These reports are integral to financial reporting vs. internal accounting, as they provide the standardized data necessary for external analysis, contrasting with the more flexible, internally-focused reports used in managerial accounting.
Key Differences Between Managerial and Financial Accounting
Understanding the key differences between managerial accounting and financial accounting is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize both internal operations and external reporting. While both disciplines deal with financial data, their objectives, reporting standards, and audiences differ significantly.
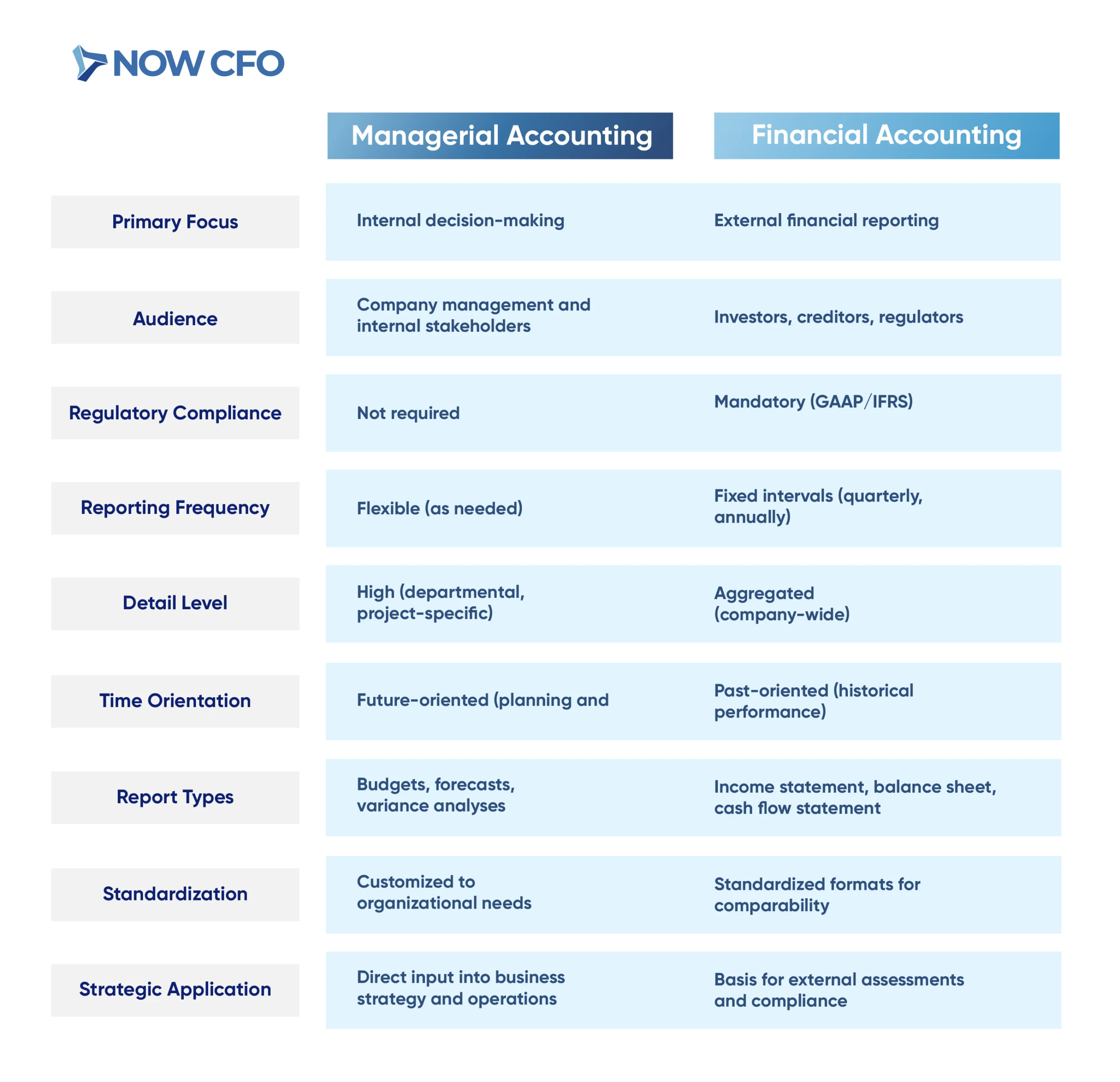
Internal vs. External Focus
Managerial accounting is designed for internal stakeholders, such as company executives and department managers. It provides detailed financial insights to aid in decision-making. In contrast, financial accounting targets external parties, offering standardized financial statements that reflect the company’s overall financial health.
Here’s a comparative overview:
| Aspect | Managerial Accounting | Financial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Audience | Internal management and employees | External stakeholders (investors, regulators) |
| Purpose | Aid in strategic planning and operational control | Provide a clear financial picture for external use |
| Reporting Detail | Detailed, segment-specific reports | Summarized, company-wide financial statements |
| Regulations | Not governed by external standards | Must comply with GAAP or IFRS |
| Frequency | As needed (e.g., daily, weekly) | Regular intervals (e.g., quarterly, annually) |
Reporting Frequency and Flexibility
Managerial accounting offers flexibility in reporting schedules, allowing businesses to generate reports as frequently as needed. This adaptability enables managers to respond swiftly to operational changes and market dynamics.
In contrast, financial accounting adheres to a fixed reporting schedule, typically quarterly or annual, to meet regulatory requirements and provide consistent information to external stakeholders.
Compliance and Standardization (GAAP/IFRS)
Financial accounting is governed by stringent compliance standards in the US and globally. These frameworks ensure consistency, reliability, and transparency in financial reporting, which is essential for maintaining investor confidence and meeting legal obligations.
Over 140 countries have adopted IFRS, highlighting its global reach, while the U.S. market, valued at $50.8 trillion, operates under GAAP. This divergence can lead to significant differences in financial metrics, with potential profit impacts of up to 25% depending on the standard applied.
In contrast, managerial accounting is not subject to external regulatory standards, allowing organizations to tailor their internal reporting practices to suit specific operational needs. This flexibility facilitates more relevant and timely information for internal decision-making, but may lack the uniformity required for external comparisons.
Data Usage in Business Strategy
Managerial accounting provides detailed financial analyses for budgeting, forecasting, and performance evaluation. By leveraging these insights, managers can identify cost-saving opportunities, allocate resources efficiently, and set realistic financial goals.
Key applications include:
- Budgeting: Developing comprehensive financial plans to guide organizational spending and investment.
- Forecasting: Predicting future financial trends based on historical data and market analysis.
- Performance Evaluation: Assessing departmental or project-specific financial outcomes to inform strategic adjustments.
These practices underscore the importance of business decision-making with accounting for sustainable growth.
Do You Need Both Managerial and Financial Accounting?
Integrating managerial accounting vs. financial accounting practices is beneficial and essential for businesses aiming for comprehensive financial oversight and strategic agility.
The synergy between these two disciplines ensures businesses meet compliance requirements while driving growth through informed strategies.
Why Businesses Should Integrate Both Accounting Types
Incorporating managerial and financial accounting allows businesses to harness each other’s strengths. Financial accounting ensures transparency and compliance, which is crucial for investor confidence and regulatory adherence.
Conversely, managerial accounting provides detailed analyses that aid in budgeting, forecasting, and operational decision-making.
By integrating these accounting types, businesses can:
- Enhance Decision-Making: Access to both historical data and real-time insights enables more informed strategic choices.
- Improve Financial Health: Combining external reporting with internal analysis helps identify cost-saving opportunities and efficiency improvements.
- Foster Transparency: Unified accounting practices ensure consistency in financial information across all levels of the organization.
This integrated approach aligns with financial reporting vs. internal accounting, bridging the gap between external compliance and internal strategy.
The Role of an Accountant in Balancing Both Functions
Accountants are pivotal in harmonizing managerial accounting vs. financial accounting functions. Their expertise ensures that financial data serves both external reporting requirements and internal management needs.
Key responsibilities include:
- Data Consolidation: Merging financial records to provide a comprehensive view for both internal and external stakeholders.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring financial reports meet legal standards while serving internal strategic purposes.
- Strategic Analysis: Interpreting financial data to guide business decisions and long-term planning.
- Budget Management: Developing and monitoring budgets, aligning with operational goals and financial constraints.
- Performance Evaluation: Assessing financial performance to identify areas for improvement and growth.
How an Outsourced CFO Can Help Manage Accounting Needs
For many SMEs, hiring a full-time CFO may not be feasible. An outsourced CFO offers a cost-effective solution, providing expert financial guidance tailored to the company’s needs.
An outsourced CFO can:
- Provide Strategic Planning: Develop long-term financial strategies that align with business objectives.
- Enhance Cash Flow Management: Implementing practices to maintain healthy cash flow, crucial for operational stability.
- Ensure Compliance: Compliance with regulatory environments to keep the business compliant with financial laws and standards.
- Offer Objective Insights: Bringing an external perspective to identify inefficiencies and opportunities for growth.
How Managerial and Financial Accounting Work Together for Business Growth
Integrating managerial accounting vs. financial accounting practices is crucial for businesses to align internal strategies with external financial realities. By leveraging financial data, companies can make informed decisions that drive growth and enhance competitiveness.
Using Financial Data for Internal Strategy Development
Financial data is a foundational element for internal strategic planning. Businesses can identify trends, assess performance, and make data-driven decisions by analyzing key financial metrics.
Key financial data points that inform business strategy include:
- Net Cash Available: Indicates the company’s financial health and ability to invest in growth opportunities.
- Revenue Growth: Helps assess market demand and sales strategies’ effectiveness.
- Profitability Ratios: Provide insights into operational efficiency and cost management.
- Economic Value-Added (EVA): Measures the value created beyond the required return of the company’s shareholders.
Leveraging Managerial Reports for External Financial Decisions
While managerial accounting primarily focuses on internal decision-making, its reports can also inform external financial decisions. Detailed managerial reports provide granular insights into cost structures, operational efficiency, and departmental performance.
For instance, a comprehensive cost analysis can reveal areas where the company can reduce expenses, thereby improving profit margins. Similarly, performance reports can highlight successful strategies that can be scaled or replicated in other business areas.
Case Study: A Business That Successfully Uses Both Accounting Methods
Amazon is a strong example of a company that effectively integrates both managerial and financial accounting to drive its operations and strategic goals.
Amazon has built an internal inventory planning system on the managerial accounting side. This system tracks real-time data on inventory levels, sales, and returns, insights that are crucial for day-to-day decision-making and long-term planning. It helps managers allocate resources efficiently, optimize logistics, and respond quickly to changing demand.
On the other hand, financial accounting is used to prepare official financial statements, like the income statement and balance sheet. These reports follow accounting rules and are shared with people outside the company, such as investors, banks, and regulators. They show how well the company is doing financially.
Common Mistakes Businesses Make When Handling Accounting
Businesses often encounter pitfalls that hinder their growth and sustainability in managerial accounting vs. financial accounting. Understanding these common mistakes is crucial for organizations to optimize their accounting practices and drive strategic success.
Focusing Only on Financial Accounting and Ignoring Managerial Insights
Many businesses prioritize financial accounting due to its role in external reporting and compliance. However, neglecting managerial accounting can lead to a lack of internal insights necessary for informed decision-making.
Relying solely on financial accounting may result in missed opportunities for cost optimization, efficiency improvements, and proactive risk management. Integrating managerial insights ensures that businesses meet external requirements and enhance internal processes and strategic planning.
Lack of Integration Between Financial and Managerial Reports
A significant oversight in many organizations is the failure to integrate financial and managerial reports, leading to fragmented data and misaligned strategies. This disconnect can cause inconsistencies in information, making it challenging for decision-makers to obtain a comprehensive view of the company’s financial health.
Key issues arising from this lack of integration include:
- Inconsistent Data: Disparate reporting systems can produce conflicting information, undermining trust in the data.
- Inefficient Decision-Making: Managers may struggle to make timely and informed decisions without a unified reporting framework.
- Strategic Misalignment: Separate reporting structures can lead to strategies that are not cohesive, affecting overall business performance.
Not Utilizing Accounting Data for Strategic Growth
Accounting data is a valuable asset that, when leveraged effectively, can drive strategic growth. However, many businesses fail to utilize this data beyond compliance purposes. To harness the full potential of accounting information, organizations should:
- Conduct Trend Analysis: Identify revenue, expenses, and cash flow patterns to forecast future performance.
- Implement Budgeting and Forecasting: Use historical data to create realistic budgets and financial projections.
- Perform Variance Analysis: Compare actual performance against budgets to identify areas needing attention.
- Assess Cost Behavior: Understand how costs change with varying activity levels to manage expenses effectively.
- Evaluate Investment Opportunities: Analyze financial data to make informed decisions about capital investments and resource allocation.
Conclusion: The Power of Using Both Accounting Types for Business Success
The synergy between managerial accounting vs. financial accounting is essential for sustainable business success. While financial accounting ensures transparency and compliance, managerial accounting provides the insights needed for strategic planning and operational efficiency.
At NOW CFO, we specialize in bridging the gap between these two accounting disciplines, offering tailored solutions that align with your business objectives. Our team of expert outsourced CFOs is equipped to provide financial clarity and strategic insight for your business to thrive.
Whether you want to streamline your financial reporting or enhance your internal decision-making processes, NOW CFO is here to assist. Contact us today to discover how our services can support your business’s financial journey.














