Internal Controls in Your Business
The importance of robust internal controls for SMEs cannot be overstated. These mechanisms are essential for ensuring financial accuracy, preventing fraud, and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.
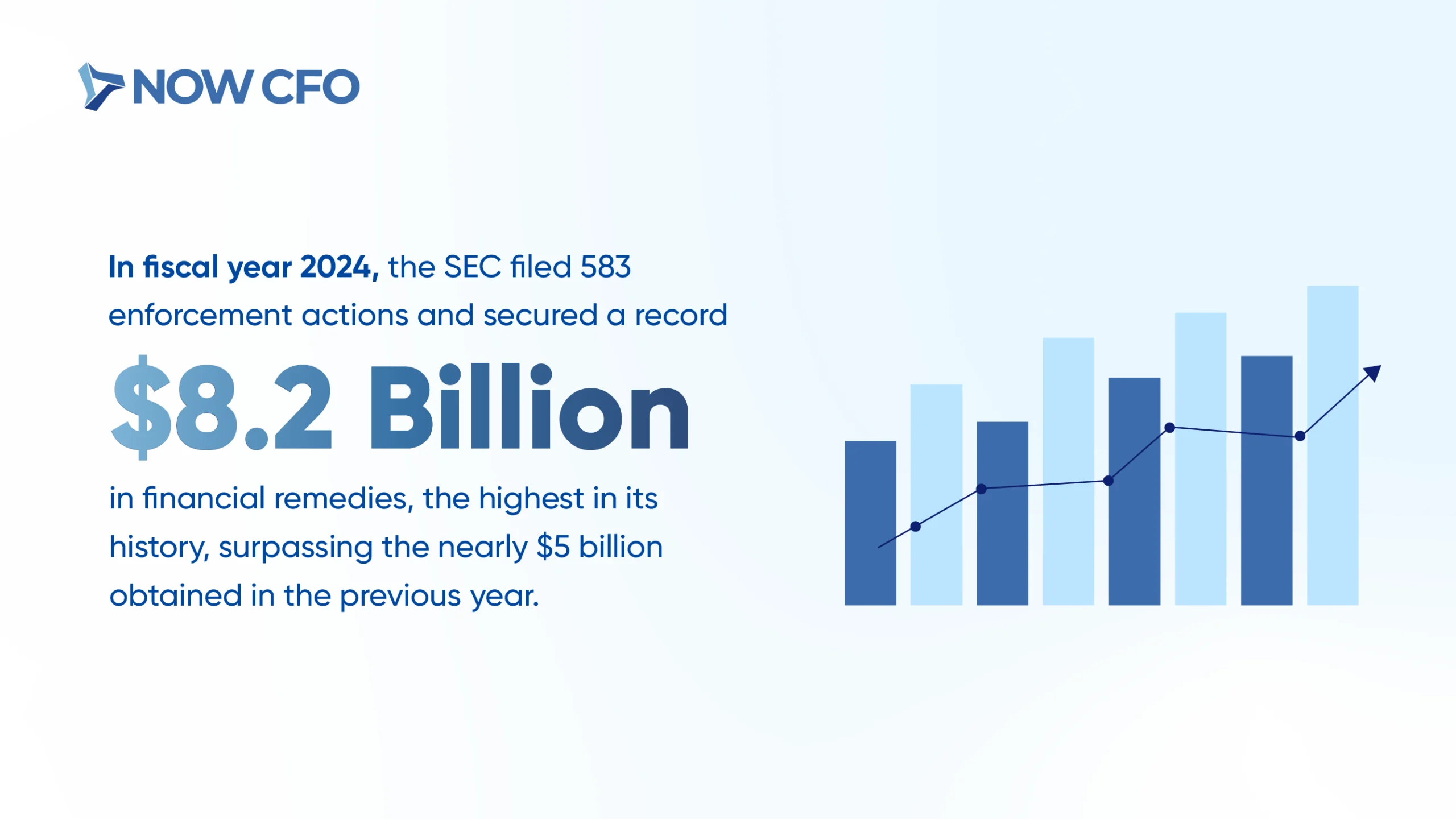
In fiscal year 2024, the SEC filed 583 enforcement actions and secured a record $8.2 billion in financial remedies, the highest in its history, surpassing the nearly $5 billion obtained in the previous year. This highlights the crucial need for businesses to implement robust internal controls to mitigate risks and maintain financial integrity.
Understanding why you need internal controls is pivotal for long-term success. These systems safeguard assets, enhance operational efficiency, and foster stakeholder confidence.
What are Internal Controls?
Internal controls are rules and procedures that help businesses run safely and accurately. They protect assets, ensure correct financial data, and support compliance with laws. These controls include approving transactions, separating duties, and checking records.
Key functions of internal controls include
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying and managing risks that could impede the achievement of organizational goals.
- Operational Efficiency: Ensuring that business processes are carried out effectively and resources are optimally used.
- Financial Reporting Accuracy: Maintaining accurate and reliable financial records to support decision-making.
- Compliance: Adhering to laws, regulations, and internal policies to avoid legal penalties and reputational damage.
Different Types of Internal Controls in Businesses
Internal controls can be categorized into several types, each serving a unique purpose within an organization’s control environment.
1. Preventive Controls: These controls are designed to deter errors or irregularities from occurring. Examples include:
- Segregation of Duties: Dividing responsibilities among individuals to reduce the risk of error or inappropriate actions.
- Authorization Controls: Requiring approval from authorized personnel before transactions are executed.
2. Detective Controls: These controls aim to identify and detect errors or irregularities that have occurred. Examples include:
- Reconciliations: Regularly comparing data from different sources to identify discrepancies.
- Audits: Conduct periodic financial statements and operations reviews to ensure accuracy and compliance.
3. Corrective Controls: These controls focus on rectifying identified issues to prevent recurrence. Examples include:
- Backup Procedures: Implementing data recovery processes to restore lost or corrupted information.
- Disciplinary Actions: Enforcing consequences for violations of policies to deter future infractions.
How Internal Controls Impact Financial Stability
Internal controls are vital in enhancing an organization’s financial stability. By ensuring accurate financial reporting, safeguarding assets, and promoting operational efficiency, these controls contribute to a business’s overall financial health.
Key impacts include
- Enhanced Reliability of Financial Reporting: Accurate financial statements are crucial for stakeholders to make informed decisions. Internal controls ensure that financial data is recorded and reported correctly, reducing the risk of misstatements.
- Fraud Prevention Strategie: Robust internal controls deter fraudulent activities by establishing clear procedures and accountability. According to the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, organizations with strong internal controls experience significantly lower fraud losses.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to laws and regulations, such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, is essential for avoiding legal penalties and maintaining investor confidence. Internal controls facilitate compliance by ensuring that financial practices align with regulatory requirements.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined processes and clear procedures reduce redundancies and errors, leading to cost savings and improved resource utilization.
Preventing Fraud and Financial Misstatements with Internal Controls
Preventing fraud and financial misstatements is a critical objective for any business aiming to maintain integrity and trust. Implementing robust internal controls is a fundamental strategy for achieving this goal.
How Internal Controls Deter Fraud in Financial Operations
Internal controls are essential in creating an environment that discourages fraudulent behavior. By systematically addressing the elements of the fraud triangle: motive, opportunity, and rationalization, internal controls minimize the chances of fraud occurring.
One of the primary ways internal controls deter fraud is by eliminating opportunities for misconduct. This is achieved through:
- Authorization Procedures: Ensuring that all transactions are approved by designated personnel before execution.
- Access Controls: Restricting access to financial systems and sensitive information to authorized individuals only.
- Audit Trails: Maintaining comprehensive records of all financial transactions to facilitate monitoring and review is one of the internal audit best practices.
Segregation of Duties to Reduce Fraudulent Activities
Building upon the foundation of internal controls, segregation of duties (SoD) is a specific strategy that plays a pivotal role in financial risk management. By dividing responsibilities among different individuals, SoD ensures that no single person has control over all aspects of any critical financial transaction.
Key aspects of SoD include:
- Transaction Authorization: One individual is responsible for approving transactions.
- Record Keeping: Another person maintains the records related to the transaction.
- Asset Custody: A separate individual handles the physical assets involved.
This division of responsibilities creates a system of checks and balances, making it more difficult for fraudulent activities to go undetected. For instance, if one employee attempts to manipulate records, another employee responsible for a different aspect of the transaction will likely notice the discrepancy.
Identifying Red Flags in Financial Transactions
In addition to establishing preventive measures, organizations must remain vigilant in detecting potential signs of fraud. Recognizing red flags in financial transactions is crucial for early intervention and mitigating fraudulent activities.
Common red flags include:
- Unusual Transaction Patterns: Transactions that occur at odd times, involve round numbers, or deviate significantly from standard patterns.
- Discrepancies in Documentation: Missing, altered, or inconsistent records that raise questions about the legitimacy of transactions.
- Employee Behavior Changes: Employees exhibiting reluctance to take vacations, living beyond their means, or displaying secretive behavior.
Internal Controls and Compliance: Meeting Regulatory Standards
Compliance with financial reporting standards is a fundamental responsibility for businesses, particularly in today’s stringent regulatory environment. Robust internal controls facilitate accurate financial reporting and help organizations avoid costly penalties.
The Role of Internal Controls in Financial Reporting Compliance
Internal controls are essential mechanisms that ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting. They encompass policies and procedures to prevent errors, detect irregularities, and safeguard assets.
Key aspects include:
- Accuracy of Financial Statements: Internal controls ensure that financial data is recorded correctly and reflects the company’s true financial position.
- Prevention of Fraud: Controls such as segregation of duties and authorization requirements deter fraudulent activities.
- Compliance with Regulations: Following standards like the SOX necessitates robust internal controls to meet compliance obligations.
According to the GAO, the SEC collected $4.1 billion in penalties for securities law violations in FY2024, highlighting the importance of compliance.
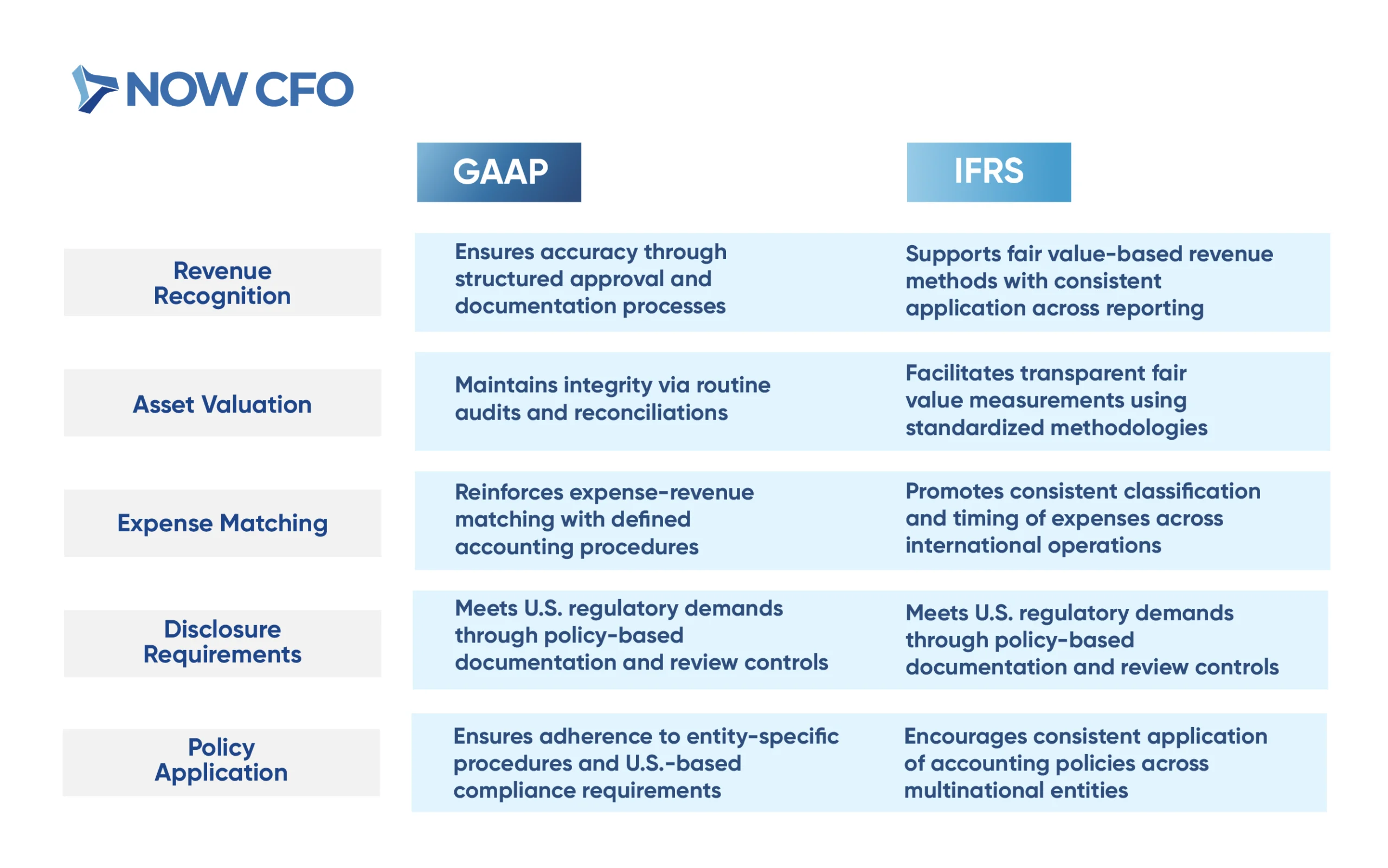
Aligning with GAAP and IFRS Requirements
Alignment with GAAP and IFRS is crucial for global financial reporting consistency. Internal controls play a pivotal role in ensuring adherence to these standards.
The following table outlines how internal controls align with key GAAP and IFRS requirements:
Avoiding Penalties and Legal Risks Through Internal Controls
Implementing robust internal controls is instrumental in mitigating legal risks and avoiding penalties associated with financial misreporting. These controls are proactive measures to detect and prevent violations that could lead to regulatory sanctions.
Key strategies include:
- Regular Audits: Conducting periodic internal and external audits to identify and rectify discrepancies.
- Compliance Monitoring: Establishing dedicated teams to oversee financial regulations and standards adherence.
- Employee Training: Educating staff on compliance requirements and ethical financial practices.
Strengthening Operational Efficiency Through Internal Controls
Businesses can significantly improve their operations by integrating automation and learning from real-world case studies.
How Internal Controls Improve Workflow and Accountability
Effective internal controls are the backbone of streamlined workflows and heightened organizational accountability. By establishing clear procedures and responsibilities, these controls minimize errors and ensure that tasks are executed efficiently.
Key benefits include:
- Standardized Procedures: Documented processes reduce ambiguity, enabling employees to perform tasks consistently and efficiently.
- Enhanced Oversight: Regular monitoring and audits ensure that operations align with organizational goals and regulatory requirements.
- Risk Mitigation: Proactively identifying and managing potential issues prevents disruptions and financial losses.
Automating Internal Controls for Better Efficiency
Transitioning from manual to automated internal controls can significantly enhance operational efficiency. Automation reduces the likelihood of human error, accelerates processes, and allows for real-time monitoring.
Advantages of automation include:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Automated systems provide instant insights into operations, facilitating prompt decision-making.
- Cost Savings: Reducing manual interventions lowers labor costs and minimizes errors that could lead to financial losses.
- Scalability: Automated controls can easily adapt to organizational growth without compromising efficiency.
Case Examples of Businesses Benefiting from Strong Internal Controls
Real-world examples underscore the tangible benefits of implementing robust internal controls:
- Bel Fuse Inc.: By enhancing its internal control systems, the company achieved greater efficiency in resource allocation and improved compliance with regulatory standards.
- Butuuro SACCO: A study revealed a significant positive relationship between a strong control environment and organizational operational efficiency.
- Commercial Banks in Ghana: Research indicated that effective internal control systems positively impact operational efficiency, reducing malfeasance and misuse of funds.
These cases illustrate how strategic implementation of internal controls can lead to enhanced operational performance and compliance.
Common Internal Control Weaknesses and How to Fix Them
Identifying and addressing internal control weaknesses is crucial for maintaining financial integrity and operational efficiency. Organizations can fortify their internal control systems by recognizing gaps in financial oversight, enhancing documentation processes, and implementing comprehensive employee training programs.
Recognizing Gaps in Financial Oversight
Financial oversight gaps often stem from insufficient segregation of duties, inadequate monitoring, and lack of timely reconciliations. These weaknesses can lead to errors, fraud, and non-compliance with regulatory standards.
Common indicators of oversight gaps include:
- Inadequate Segregation of Duties: When a single employee controls multiple financial processes, such as authorization and record-keeping, it increases the risk of undetected errors or fraud.
- Lack of Regular Reconciliations: Failing to perform timely reconciliations between accounts can result in unnoticed discrepancies and financial misstatements.
- Insufficient Monitoring: Without ongoing monitoring of financial activities, organizations may overlook irregularities that could indicate deeper issues.
Strategies to address these gaps:
- Implement Segregation of Duties: Assign different individuals to authorize transactions, record them, and handle related assets.
- Establish Regular Reconciliation Processes: Schedule periodic reconciliations to ensure that all financial records are accurate and up to date.
- Enhance Monitoring Mechanisms: Utilize internal audits and real-time monitoring tools to detect and address anomalies promptly.
Enhancing Documentation and Reporting Processes
Robust documentation and reporting are fundamental to effective internal controls. They provide a clear audit trail, facilitate compliance, and support informed decision-making.
Key components of effective documentation:
- Comprehensive Policies and Procedures: Clearly defined policies ensure consistency and guide employees.
- Accurate Record-Keeping: Maintaining detailed records of all transactions supports transparency and accountability.
- Regular Updates: Keeping documentation current reflects process changes and regulatory requirements.
Best practices for enhancing documentation:
- Standardize Documentation Formats: Use uniform templates for policies, procedures, and records to ensure consistency.
- Implement Document Management Systems: Utilize digital tools to store, organize, and retrieve documents efficiently.
- Conduct Regular Reviews: Periodically assess and update documentation to align with current practices and regulations.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs for Internal Controls
Transitioning from process improvements to personnel development, employee training, and awareness is pivotal in reinforcing internal controls. Educated employees are better equipped to adhere to policies, recognize potential issues, and contribute to a culture of accountability.
Benefits of comprehensive training programs:
- Enhanced Understanding of Controls: Employees gain clarity on internal control procedures and their roles.
- Improved Compliance: Training ensures that staff know regulatory requirements and organizational policies.
- Increased Risk Awareness: Educated employees are more likely to identify and report irregularities, reducing the risk of fraud.
Strategies for implementing effective training:
- Develop Tailored Training Programs: Customize training content to address specific organizational roles and responsibilities.
- Utilize Interactive Training Methods: Incorporate workshops, simulations, and e-learning to engage employees and reinforce learning.
- Assess Training Effectiveness: Regularly evaluate training programs through assessments and feedback to ensure they meet organizational needs.
How an Outsourced CFO Can Help Strengthen Internal Controls
SMEs increasingly turn to outsourced CFOs to bolster their internal control systems. These professionals bring a wealth of experience and strategic insight, enabling organizations to enhance financial oversight, implement robust risk management strategies, and ensure scalability while maintaining compliance with evolving regulations.

Assessing and Improving Existing Internal Control Frameworks
An outsourced CFO begins by comprehensively assessing a company’s current internal control environment. This evaluation identifies weaknesses, inefficiencies, and areas susceptible to risk.
Key steps in this process include:
- Process Mapping: Documenting existing financial processes to identify gaps and redundancies.
- Control Testing: Evaluating the effectiveness of current controls through testing and analysis.
- Recommendations: Providing actionable insights to enhance control activities and monitoring mechanisms.
Implementing Risk Management Strategies
By identifying potential financial, operational, and compliance risks, an outsourced CFO establishes protocols to mitigate these threats effectively.
Key components of risk management include:
- Risk Identification: Analyzing internal and external factors that could impact financial stability.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of identified risks.
- Risk Mitigation: Developing policies and procedures to minimize or eliminate risks.
- Monitoring and Review: Continuously tracking risk factors and adjusting strategies as needed.
Ensuring Scalability and Compliance with Financial Regulations
Outsourced CFOs provide the expertise to ensure that internal controls scale appropriately and adhere to applicable laws and standards.
Strategies to achieve scalability and compliance:
- Regulatory Alignment: Ensuring financial practices comply with relevant laws and industry standards.
- Technology Integration: Implementing scalable financial systems that support compliance and efficiency.
- Policy Development: Establishing clear policies and procedures to guide financial operations.
- Training and Education: Providing ongoing education to staff on compliance requirements and best practices.
Partnering with NOW CFO for Enhanced Internal Controls
NOW CFO offers specialized outsourced CFO services to strengthen internal controls and drive business success. With a team of experienced professionals, we provide tailored solutions that address each organization’s unique challenges.
Benefits of partnering with NOW CFO:
- Expertise: Access to seasoned financial professionals with diverse industry experience.
- Customization: Solutions tailored to your business’s specific needs and goals.
- Efficiency: Streamlined processes that enhance financial reporting and operational performance.
- Compliance: Assurance that financial practices meet regulatory standards and requirements.
Conclusion: Securing Your Business with Strong Internal Controls
Recognizing the importance why you need internal controls is the first step toward fortifying your business against potential risks. Companies can achieve greater transparency, accountability, and resilience by investing in comprehensive internal control systems.
To embark on this journey toward enhanced financial governance, consider partnering with NOW CFO’s experts specializing in internal control frameworks. Schedule a free consultation to strengthen your internal controls and secure your business’s future.














