In financial management, “data fortresses” are robust measures and systems designed to protect sensitive information, including financial information. These fortresses are essential in safeguarding data against unauthorized access and breaches. Maintaining confidentiality in financial statements is a regulatory requirement and a cornerstone of building stakeholder trust.
Understanding Confidentiality in Financial Statements
Confidentiality in financial statements is critical for protecting sensitive information and maintaining business integrity. Key aspects of confidentiality include:
- Definition of Confidentiality: Maintaining confidentiality refers to keeping sensitive information private and secure, accessible only to authorized individuals. In financial statements, this means protecting information such as revenue figures, profit margins, and strategic business plans. Such information could harm a company’s competitive advantage and operational integrity if exposed.
- Types of Confidential Information: Various types of financial information require protection. Revenue figures provide insights into a company’s financial health and performance. Profit margins reveal the efficiency and profitability of business operations. Strategic plans outline future business directions and competitive strategies. Protecting this information is crucial to maintaining stakeholder confidence.
Risks to Confidential Financial Information
Confidential financial information is constantly at risk from various threats. Understanding these risks helps you to protect sensitive data. The primary risks include:
- Internal Threats: Employees, intentionally or accidentally, can pose significant risks to data confidentiality. Unauthorized access or inadvertent leaks of financial data can lead to severe consequences. For instance, employees with access to sensitive financial information may engage in insider trading or share confidential data with competitors. An accidental email containing sensitive financial information could also be sent to an unauthorized recipient, resulting in the unintended exposure of critical data. This is why it’s important to have internal controls in your business.
- External Threats: Cyberattacks, data breaches, and industrial espionage are external threats that constantly endanger financial information. Malicious actors often target financial data to exploit or ransom it, causing substantial damage to businesses. It’s important to note that these attacks are happening more often. In 2023, data breaches rose 20% from 2022. Hackers may deploy malware to infiltrate financial systems and steal sensitive information, which can then be sold on the dark web or used to extort the company. Moreover, sophisticated phishing attacks can deceive employees into revealing their login credentials, granting cybercriminals access to confidential financial records.
- Consequences of Breaches: Breaches in confidentiality can lead to financial loss, legal penalties, and irreparable reputational damage. The cost of recovering from such breaches often far exceeds the investment in preventive measures. When confidential financial data is compromised, a company may face lawsuits, regulatory fines, and a significant loss of customer trust. This can result in decreased business opportunities and long-lasting negative effects on the company’s operations and profitability. Additionally, the time and resources spent dealing with the aftermath of a breach can divert attention from core business activities, further impacting overall performance.
Establishing a Data Fortress: Best Practices
Building a robust data fortress involves several key best practices. These practices guarantee that financial information remains secure and confidential:
- Access Controls: Strong access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can access your data. Businesses can tightly regulate who can view or modify critical information using role-based access controls and multi-factor authentication. Access logs and monitoring can also help track unauthorized access attempts.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting all your data is crucial. Encryption converts data into an unreadable, secure format without the correct decryption key, thus protecting it from unauthorized access. This practice confirms that data remains protected and unusable even if unauthorized individuals intercept it. Advanced encryption standards (AES) and public key infrastructure (PKI) are commonly used methods that offer robust protection.
- Secure Communication Channels: Secure communication channels for sharing sensitive information prevent interception and unauthorized access during transmission. Technologies such as VPNs and SSL ensure that data shared over networks is encrypted and secure from eavesdropping. Additionally, implementing end-to-end encryption for emails and messaging services further safeguards communications.
- Regular Audits: Regular audits and monitoring activities help detect and address potential vulnerabilities, ensuring ongoing compliance and security. Audits provide insights into security posture, reveal areas for improvement, and confirm that security measures are effective. Regular vulnerability assessments can uncover weaknesses before malicious actors exploit them.
Policies and Procedures
Effective policies are the foundation of maintaining confidentiality efforts. Here are the key elements that organizations should focus on to protect financial data:
- Data Governance Policies: Organizations should have comprehensive policies outlining measures for protecting financial data. These policies should cover data classification, access controls, and incident response protocols. Companies can minimize the risk of potential breaches by clearly defining how data should be handled and who has access to it. Regular updates to these policies guarantee they remain effective against evolving threats.
- Employee Training: Training employees on data confidentiality and security practices is vital. Educated employees will recognize and mitigate more risks. Regular training sessions on the latest security practices ensure that employees remain vigilant and informed about potential threats. This training should include recognizing phishing attempts, securing personal devices, and properly handling sensitive information both in digital and physical forms.
- Incident Response Plan: An incident response plan ensures that the organization can quickly contain the damage. The plan should include steps for identifying the breach, notifying affected parties, and restoring data security. Regular drills and updates to the incident response plan help maintain its effectiveness and guarantee that all team members are prepared to act during a breach.
Leveraging Technology for Confidentiality
Advancements in technology offer powerful tools and methods to enhance the confidentiality of financial statements. Below are some key technologies and their roles in safeguarding financial information:
- Cybersecurity Tools: Utilizing various cybersecurity tools can significantly bolster the defense of financial information. These tools integrate to create multiple layers of security, making it more difficult to access sensitive data.
- Cloud Security: Cloud services offer scalable and robust security measures for storing financial data. However, organizations must be wary of cloud providers’ security practices to maintain data protection. Cloud security includes data encryption, secure access controls, and regular security audits to ensure ongoing data integrity and confidentiality.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology provides a tamper-proof way to store and manage financial data. Its inherent security features, such as immutability and consensus mechanisms, make it an excellent option for enhancing data integrity and confidentiality. Using blockchain, businesses can guarantee that financial data remains secure and unaltered, fostering trust and transparency.
Establishing and maintaining data fortresses is paramount for the confidentiality of financial statements. By understanding the risks, implementing best practices, developing strong policies, and leveraging advanced technologies, businesses can protect their sensitive financial information and maintain the trust of their stakeholders.
Fractional CFO Can Be Benefit to Your Business
Many SMEs face financial challenges that can impede growth and sustainability. Notably, 44% of early startup closures are attributed to a lack of cash flow management.

Engaging a fractional CFO has become an increasingly popular solution to these challenges. A fractional CFO provides part-time expert financial oversight, offering strategic planning, cash flow optimization, and financial reporting without the commitment of a full-time executive.
This approach allows businesses to access high-level financial expertise tailored to their needs, facilitating informed decision-making and fostering sustainable growth.
What is a Fractional CFO, and How Do They Work?
Companies often seek financial expertise without the commitment of a full-time executive. This is where a fractional CFO comes into play.
Understanding the Role of a Fractional CFO
A fractional CFO is a financial expert who provides executive-level guidance on a part-time or project basis. Unlike traditional full-time CFOs, they offer strategic financial planning, analysis, and oversight tailored to the company’s needs.
This flexibility allows businesses to access high-level financial acumen without the overhead of a permanent position.
Key responsibilities include:
- Financial Strategy Development: Crafting long-term financial plans aligned with business objectives.
- Cash Flow Management: Ensuring liquidity and optimal allocation of resources.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Preparing detailed budgets and financial forecasts to guide decision-making.
- Risk Management: Identifying financial risks and implementing mitigation strategies.
How Fractional CFO Services Differ from Full-Time CFOs
While both roles aim to enhance a company’s financial health, there are distinct differences between fractional CFOs and full-time CFOs.
Fractional CFOs:
- Cost-Effective: Engaged as needed, reducing salary and benefit expenses.
- Flexible Engagements: Adaptable to the company’s evolving requirements for specific projects or ongoing support.
- Diverse Expertise: Often brings experience from various industries, offering a broad perspective.
Full-Time CFOs:
- Permanent Presence: Fully integrated into the company’s daily operations.
- Higher Cost: Command a full-time salary with associated benefits.
- Industry-Specific Focus: Typically possess deep expertise in a single industry.
Why Businesses are Turning to Fractional CFOs
The trend toward hiring fractional CFOs is gaining momentum, especially among SMEs. SMEs that employ part-time CFO services experience an increase in profitability.
Reasons for this shift include:
- Scalability: Businesses can adjust the level of financial oversight as they grow.
- Access to Expertise: Even startups can benefit from seasoned financial professionals without long-term commitments.
- Cost Savings: Allocating resources to a fractional CFO can be more economical than hiring a full-time executive, especially when full-time oversight isn’t necessary.
Key Benefits of Hiring a Fractional CFO
Engaging a fractional CFO offers numerous advantages for businesses seeking top-tier financial leadership without the commitment of a full-time executive.
Cost-Effective Financial Leadership
Hiring a full-time Chief Financial Officer can be a significant financial burden, especially for SMEs. According to Yale University’s Ledger, an average C-level executive commands a minimum of $250,000 annually, excluding benefits and taxes.
In contrast, a fractional CFO provides part-time access to high-level financial expertise, allowing businesses to benefit from seasoned leadership without incurring the full salary and associated costs.
Advantages include:
- Reduced Overhead: Pay only for the services you need, scaling up or down based on business requirements.
- No Additional Benefits: Avoid health insurance, retirement plans, and other employee benefits expenses.
- Immediate Expertise: Access experienced professionals without the time and costs associated with recruitment and onboarding.
Expertise in Cash Flow Management
Effective cash flow management is crucial for business sustainability and growth. A fractional CFO brings specialized skills to monitor, analyze, and optimize cash flow, ensuring the company maintains adequate liquidity to meet its obligations and invest in opportunities.
Key contributions include:
- Cash Flow Forecasting: Developing projections to anticipate cash shortages or surpluses.
- Working Capital Optimization: Implementing strategies to efficiently manage receivables, payables, and inventory.
- Expense Control: Identifying areas to reduce costs without compromising quality or growth.
By leveraging these strategies, businesses can enhance their financial stability and make informed operational decisions.
Strategic Financial Planning and Budgeting
Long-term success requires careful planning and resource allocation. A fractional CFO assists in crafting comprehensive financial plans and budgets that align with the company’s strategic objectives.
Services offered:
- Goal Setting: Defining clear financial targets based on market analysis and business aspirations.
- Budget Development: Allocating resources effectively across departments and projects.
- Performance Monitoring: Regularly reviewing financial metrics to ensure adherence to the plan and making adjustments as necessary.
Improved Financial Reporting and Decision-Making
Accurate and timely financial reporting is essential for informed decision-making. A fractional CFO ensures that financial statements and reports are precise, compliant, and reflective of the company’s actual financial position.
Benefits include:
- Enhanced Transparency: Clear reporting fosters stakeholder trust and aids in strategic planning.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring all financial practices meet current laws and standards, reducing the risk of legal issues.
- Data-Driven Insights: Utilizing financial data to guide decisions on investments, expansions, and other critical business moves.
Companies can make strategic decisions that drive growth and profitability with improved reporting.
Risk Management and Compliance Support
Dealing with financial regulations and potential risks requires specialized knowledge. A fractional CFO provides expertise in identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks while ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Key areas of focus:
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating financial vulnerabilities related to market fluctuations, credit exposures, and operational inefficiencies.
- Internal Controls: Establishing robust processes to prevent fraud and ensure the accuracy of financial data.
- Regulatory Adherence: Keeping abreast of changes in financial laws and ensuring the company’s practices remain compliant.
When Should a Business Consider a Fractional CFO?
Determining the optimal time to engage a fractional CFO is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance their financial management without the commitment of a full-time executive.
Signs Your Business Needs CFO-Level Support
Recognizing the indicators that your company requires advanced financial expertise can prompt timely intervention. One significant sign is rapid growth, which often leads to increased financial complexity.
Additionally, the need for strategic financial oversight becomes evident if your business prepares for significant financial events, such as mergers or acquisitions. Moreover, inadequate financial reporting hindering informed decision-making indicates that CFO-level support is necessary.
Key indicators include:
- Rapid Expansion: Growth leading to complex financial operations.
- Major Financial Transactions: Plans for mergers, acquisitions, or significant capital investments.
- Inadequate Financial Reporting: Lack of detailed insights impeding strategic decisions.
According to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, small business owners are over 20 percentage points more likely to experience income volatility than non-owners, underscoring the need for professional financial management.
Growth Challenges That Require Strategic Financial Guidance
As businesses scale, they often encounter challenges that necessitate strategic financial planning. Managing increased operational costs, optimizing cash flow, and ensuring sustainable profitability become paramount.
A fractional CFO offers the expertise to counter these complexities, providing tailored strategies that align with the company’s growth objectives.
Challenges addressed by a fractional CFO:
- Operational Cost Management: Identifying and controlling escalating expenses.
- Cash Flow Optimization: Ensuring sufficient liquidity for ongoing operations and investments.
- Profitability Analysis: Assessing product or service lines to maximize margins.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation’s 2024 Small Business Lending Survey highlights that while most banks are adopting new technologies, small business lending continues to be relationship-oriented and staff-intensive.
Managing Financial Complexity Without a Full-Time Hire
Not all businesses have the resources or need a full-time Chief Financial Officer. In such cases, a fractional CFO provides a cost-effective solution by delivering high-level financial oversight part-time.
This arrangement allows companies to benefit from expert financial management without the financial commitment associated with a full-time executive role.
Benefits of a fractional CFO:
- Flexibility: Engage services as needed, scaling with business demands.
- Cost Savings: Access top-tier expertise without incurring full-time salary and benefits.
- Specialized Knowledge: Benefit from the CFO’s experience across various industries and financial scenarios.
How a Fractional CFO Helps with Business Growth
Engaging a fractional CFO can significantly accelerate business growth by providing expert financial guidance without the commitment of a full-time executive.

Scaling Operations with Financial Insights
As businesses expand, financial complexities often increase. A fractional CFO offers strategic insights to counter these challenges effectively. They analyze economic data to identify trends, optimize cash flow, and allocate resources efficiently.
This proactive approach facilitates informed decision-making, enabling companies to scale operations sustainably.
Key contributions include:
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Developing detailed financial projections to guide growth strategies.
- Cost Management: Identifying areas to reduce expenses without compromising quality.
- Performance Metrics: Establish KPIs to monitor progress and adjust plans.
Raising Capital and Managing Investor Relations
Securing funding is often a critical component of business expansion. A fractional CFO brings fundraising and investor relations expertise, enhancing a company’s ability to attract and retain investment.
Services provided:
- Financial Documentation: Preparing comprehensive financial statements and projections that appeal to potential investors.
- Investor Presentations: Crafting compelling narratives highlighting the company’s value proposition.
- Due Diligence Support: Ensuring all financial records are accurate and transparent, facilitating smoother investment processes.
Optimizing Profitability and Cost Efficiency
Enhancing profitability while maintaining cost efficiency is a delicate balance. A fractional CFO provides the expertise to achieve this equilibrium through strategic financial management.
Approaches include:
- Margin Analysis: Evaluating product or service lines to determine profitability and make informed decisions about pricing or discontinuation.
- Expense Auditing: Reviewing operational costs to identify and eliminate inefficiencies.
- Process Improvement: Implementing streamlined workflows to reduce waste and enhance productivity.
Choosing the Right Fractional CFO for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate fractional CFO is a pivotal decision that can significantly influence your company’s financial health and strategic direction.
Qualities to Look for in a Fractional CFO
Identifying the right qualities in a fractional CFO ensures they can effectively contribute to your business’s success.
Key attributes include:
- Financial Expertise: A strong background in financial management, including budgeting, forecasting, and cash flow analysis, is essential.
- Strategic Thinking: The ability to align financial strategies with business objectives, providing insights that drive growth and profitability.
- Communication Skills: Proficiency in understanding complex financial concepts to stakeholders at all levels.
- Technological Proficiency: Familiarity with modern financial software and data analytics tools to enhance reporting accuracy and efficiency.
- Flexibility: Adaptability to the evolving needs of your business, offering scalable solutions as your company grows.
Questions to Ask Before Hiring a Fractional CFO
Conducting a thorough interview is crucial to ensure the candidate’s suitability for your business.
Consider asking:
What experience do you have with companies at my growth stage?
Understanding their familiarity with businesses similar to yours can provide confidence in their capability to address your specific challenges.
Can you help with my specific financial challenges?
Assess whether their expertise aligns with your current financial concerns, such as cash flow management or fundraising.
How do you typically work with clients?
Clarify their working style, availability, and approach to ensure it complements your company’s culture and expectations.
What industries do you specialize in?
Industry-specific knowledge can be invaluable, as it ensures that the CFO is aware of the unique financial dynamics and regulatory requirements pertinent to your sector.
Can you assist with raising capital?
If growth plans involve securing funding, their experience in fundraising and investor relations is crucial.
These questions will provide deeper insights into the candidate’s suitability and how they can add value to your business.
How to Ensure a Good Fit for Your Business Needs
Ensuring alignment between the fractional CFO and your business is vital for a successful partnership.
Steps to achieve this include:
- Define Your Objectives: Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with their engagement, be it improving cash flow, preparing for expansion, or enhancing financial reporting.
- Assess Cultural Fit: Ensure their working style and values align with your company culture, facilitating smoother collaboration.
- Check References: Speak with previous clients to gauge their performance, reliability, and impact on past engagements.
- Set Clear Expectations: Establish the scope of work, communication channels, and performance metrics from the outset to avoid misunderstandings.
Conclusion: Unlocking Financial Success with a Fractional CFO
Partnering with a Fractional CFO can significantly enhance your company’s financial health and strategic direction. At NOW CFO, we specialize in providing outsourced CFO services customized to meet your business’s unique needs.
Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to delivering actionable financial insights and strategies that drive success. We invite you to schedule a free consultation to discover how our services can benefit your organization. Contact us to connect with our experts and take the first step toward achieving your financial goals.
An interim controller is a financial expert brought into a business temporarily to manage and oversee the company’s financial operations. Unlike a permanent controller, an interim controller is typically hired to address short-term needs during transitions or unexpected departures. This role is important in maintaining the stability and accuracy of financial reporting during periods of change.
When to Consider Hiring an Interim Controller
Hiring an interim controller can be a strategic move for various business scenarios. Here are some key situations where an interim controller can be particularly beneficial:
- During Leadership Transitions: When a company undergoes leadership transitions, such as a change in CFO or CEO, maintaining financial stability is crucial. An interim controller can provide the needed expertise to ensure that financial operations continue smoothly during this period of change, minimizing disruptions and maintaining stakeholder confidence. With so many businesses undergoing leadership transitions, the demand for positions like the interim controller has risen by 114%.
- Sudden Departures: If a permanent controller leaves the company unexpectedly, an interim controller can swiftly fill the gap. This immediate support helps prevent any lapses in financial oversight, ensuring that reporting, budgeting, and compliance tasks are managed without interruption.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: M&As often involve complex financial challenges. An interim controller can offer the specialized knowledge to navigate these complexities, assist with due diligence, integrate financial systems, and ensure that all aspects of the transaction are handled efficiently.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
An interim controller is tasked with a variety of responsibilities to ensure the financial health and stability of a business. Here are the core responsibilities they typically handle:
- Financial Reporting: Interim controllers are responsible for accurately and timely reporting financial data. This involves preparing reports that reflect the company’s financial performance and ensuring that all financial statements are accurate and comply with regulatory standards.
- Budgeting: Creating and managing budgets is another critical responsibility. Interim controllers develop comprehensive budgets that align with the company’s strategic goals and monitor actual performance against these budgets, making adjustments as necessary.
- Compliance: Compliance with financial regulations is essential. Interim controllers must stay up-to-date with the latest regulatory changes and ensure that the company’s financial practices adhere to these requirements to avoid legal issues and penalties.
- Month-End and Year-End Closings: Interim controllers oversee the month-end and year-end closing processes. This includes reconciling accounts, reviewing financial statements for accuracy, and ensuring that all financial data is properly recorded and reported.
- Preparing Financial Statements: Preparing financial statements is a key duty. Interim controllers generate accurate income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, providing a clear picture of the company’s financial position.
- Overseeing Audits: Interim controllers also oversee internal and external audits. They ensure that all financial records are in order and assist auditors by providing documentation and explanations to facilitate a smooth audit process.
Skills and Qualifications
Several skills and qualifications must be considered when selecting a controller. These attributes ensure that the interim controller can effectively manage your financial operations and contribute to the overall stability of your business. The key skills and qualifications include:
- Analytical Abilities: An interim controller’s strong analytical abilities are crucial. This skill enables them to assess complex data and make informed decisions that benefit the company. A controller with excellent analytical skills can quickly pinpoint issues and propose effective solutions.
- Proficiency in Accounting Software: Accounting software is another qualification. An interim controller must be adept at using various accounting tools and platforms to manage financial records, generate reports, and ensure accurate data entry. Familiarity with the latest software can streamline financial processes and enhance efficiency.
- Understanding Financial Regulations and Standards: An interim controller must deeply understand financial regulations and standards. This helps maintain compliance with state and federal regulations and avoid costly fines and penalties. The interim controller must also stay updated with regulation changes to ensure the company’s adherence to all necessary guidelines.
- Industry-Specific Experience: Industry-specific experience can be incredibly valuable for a controller. Familiarity with your sector’s financial challenges and nuances allows the interim controller to adapt quickly and provide more relevant insights and strategies. This can significantly reduce the learning curve and enhance the overall effectiveness of the interim controller’s contributions.
Benefits of an Interim Controller
Hiring an interim controller can offer several distinct advantages for your business. These benefits can help you manage financial operations more effectively and efficiently, especially during transitional periods. Below are some key benefits explained in detail:
- Flexibility and Scalability: An interim controller allows you to manage your financial operations according to your business. Whether you require someone for a few months during a busy period or a longer term during a major transition, an interim controller can scale their involvement to meet your requirements. This adaptability ensures that your financial processes remain robust and responsive to your business’s demands.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Employing a controller can be more economical than hiring a full-time controller, particularly if your need for their expertise is short-term. You can avoid the long-term commitment and costs associated with a permanent hire, such as benefits and ongoing salary, while gaining access to high-level financial aid.
- Fresh Perspective and New Insights: An interim controller brings fresh eyes to your financial operations. Their external viewpoint can help identify inefficiencies, uncover opportunities for improvement, and introduce best practices that your team may have yet to consider. This new perspective can significantly enhance your financial management and overall business performance.
Challenges and Considerations
While hiring an interim controller offers many benefits, you must be aware of potential challenges and plan accordingly. Here are some key considerations:
- Integration into Existing Team and Processes: Integrating an interim controller into your existing team and processes can take time. Providing a thorough onboarding process is crucial to ensure they understand your company’s financial systems and culture. Clear expectations and support facilitate a smoother transition.
- Learning Curve and Familiarization: An interim controller may face a learning curve as they familiarize themselves with your business. Providing access to detailed documentation and key team members can help them quickly get up to speed, reducing the time needed to become fully effective.
- Ensuring Effective Communication and Collaboration: Good communication and collaboration ensure the success of an interim controller. Establishing regular check-ins and fostering an open line of communication with your interim controller can help address any issues promptly and ensure they are well-integrated into your financial operations.
An interim controller can play a vital role in maintaining your business’s financial stability and integrity during periods of change. By understanding the key responsibilities, benefits, and potential challenges for your business, you can make better decisions. Strategically using an interim controller can give your business the stability to navigate financial transitions successfully.
Need help finding an interim controller? Contact a NOW CFO specialist for more information.
Learn More: What is A Financial Controller
Did you know that 80% of businesses operate without a CFO? A permanent CFO can be expensive, leaving some owners unsure of how to control their financial health. Unlike a permanent CFO, an interim CFO is hired to address immediate financial challenges and opportunities, often during transition or change. This temporary role allows businesses to benefit from high-level financial leadership without committing to a long-term employment contract.
Reasons for Hiring an Interim CFO
Hiring an interim CFO can be a strategic decision for companies facing various challenges and opportunities. Here are some common scenarios where an interim CFO can be particularly beneficial:
- The sudden departure of the CFO: When a permanent CFO leaves unexpectedly, an interim CFO can temporarily assume financial leadership. This prevents disruptions in financial operations and provides time to find a suitable long-term replacement.
- Transitional periods: An interim CFO can offer the expertise needed to navigate these transitions smoothly during significant changes, such as restructuring or market shifts. Their experience can help stabilize the company and maintain investor confidence.
- Mergers and acquisitions: An interim CFO can play an important role during mergers and acquisitions by managing due diligence, financial analysis, and integration processes. Their objective perspective can facilitate smoother transactions and better alignment of financial strategies.
- Rapid growth: Companies undergoing rapid growth may require help managing their finances efficiently. An interim CFO can implement robust financial systems, enhance cash flow management, and create sustainable growth without compromising financial health.
- Financial restructuring: when financially distressed or restructuring, an interim CFO can provide and execute turnaround strategies. Their cost management, debt restructuring, and financial planning skills are invaluable in restoring financial stability.
Key Responsibilities of an Interim CFO
The responsibilities of an interim CFO are comprehensive and include maintaining the financial health of any corporation. Key responsibilities include:
- Financial management and oversight: An interim CFO ensures accurate and timely financial reporting, budgeting, and performance tracking. They establish robust financial controls, monitor expenditures, and provide insights into cost-saving opportunities. Their oversight extends to managing accounting teams and maintaining financial policy and procedure adherence.
- Strategic planning and execution: An interim CFO develops and implements financial strategies aligned with the enterprise’s long-term objectives. They work closely with senior management to set financial goals, create budgets, and develop forecasts. Leveraging their strategic insights, they help guide your team through growth phases, market expansions, and other significant organizational initiatives.
- Cash flow management and forecasting: Effective cash flow management is vital for any business. An interim CFO monitors and manages cash flow so that the company can meet its obligations. They analyze cash flow patterns, forecast future cash needs, and implement strategies to optimize liquidity, such as adjusting payment terms or securing short-term financing.
- Financial reporting and compliance: Ensuring compliance with financial regulations and standards is another key responsibility. An interim CFO prepares accurate financial statements, oversees audits, and checks that all financial activities comply with relevant laws and regulations. This role helps maintain financial integrity and keep legal issues at arm’s length.
- Risk management and mitigation: Identifying and working to mitigate financial risks is a fundamental practice for protecting your assets. An interim CFO conducts risk assessments, implements internal controls, and develops contingency plans to address potential financial disruptions. This proactive approach helps safeguard your financial stability.
- Investor relations and fundraising: An interim CFO manages investor relationships and secures necessary funding to support operations and growth. They communicate your financial health and strategic direction to investors, prepare detailed financial reports, and engage in fundraising activities to attract investment capital or secure loans.
Skills and Qualities of an Effective Interim CFO
An effective interim CFO brings distinctive skills that allow them to produce positive outcomes for your corporation. Here are the essential skills and qualities in more detail:
- Financial Expertise: An interim CFO must deeply understand financial management, accounting principles, and corporate finance. This includes budgeting, forecasting, financial analysis, and financial reporting knowledge, making their ability to grasp your financial situation quickly and identify areas for improvement quite valuable.
- Strategic Thinking: Thinking strategically is a key attribute of an interim CFO. They must be able to develop and implement long-term financial strategies that work towards the overall objectives. This involves understanding the current financial landscape and anticipating future trends and challenges, allowing you to stay ahead of the curve.
- Leadership: Strong leadership skills are required for an interim CFO. They must be able to guide and influence the finance team and other executives to achieve your financial goals. Effective leadership involves clear communication, setting expectations, and fostering a culture of accountability and performance.
- Adaptability: An interim CFO must be highly adaptable and able to acclimate to new environments and business challenges quickly. This flexibility allows them to hit the ground running and make immediate contributions, regardless of the company’s current state. Their ability to manage change and navigate uncertainty is critical for success in this role.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: Identifying issues and developing effective solutions is a hallmark of an effective interim CFO. They must be able to analyze complex financial problems, consider multiple perspectives, and implement practical and impactful solutions. This skill is particularly needed in times of financial distress or significant change.
- Communication Skills: Communication skills are paramount for an interim CFO. They must convey complex information clearly and concisely to stakeholders, including executives, board members, employees, and investors. Strong communication can also help build relationships and foster collaboration within the corporation.
Integration with the Existing Team
Integrating an interim CFO into the existing management team is crucial for ensuring their success and maximizing their impact. Here are key strategies for effective integration:
- Clear Communication of Role and Objectives: Clearly define the interim CFO’s responsibilities and goals for the organization. Ensure all team members understand the interim CFO’s mandate and how it aligns with the company’s overall strategy.
- Fostering an Environment of Collaboration: Encourage open communication and collaboration between the interim CFO and existing team members. Promote a culture of teamwork to facilitate a smooth working relationship.
- Building Trust with Executives and Employees: Establish trust by involving the interim CFO in key meetings and decision-making processes. Create opportunities for the interim CFO to demonstrate their commitment to your success.
- Providing Necessary Resources and Support: The interim CFO must access all the necessary resources, including financial data, tools, and support staff. Facilitate introductions and integration into your workflows and systems.
- Setting Up Regular Check-ins and Feedback Loops: Schedule meetings to discuss progress, challenges, and feedback. Maintain open lines of communication so that any concerns are addressed promptly and better, guaranteeing alignment with objectives.
An interim CFO is key for businesses facing financial challenges or transitions. By leveraging the leadership of an interim CFO, companies can navigate through difficult periods, stabilize their financial operations, and achieve growth and success. An interim CFO can be the key to unlocking your company’s potential during times of change.
Need help finding an interim CFO for your organization? Contact a NOW CFO specialist for more information.
Learn More: The Role of An Interim Controller in Your Business
Benefits of Outsourcing Accounts Payable
Outsourcing accounts payable can be a game-changer for companies looking to enhance their financial operations. Entrusting this critical function to external experts can unlock various benefits that drive efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings. Let’s explore the key advantages of outsourcing accounts payable and how it can transform your business.
Outsourcing Accounts Payable (AP) and Cost Savings
Outsourcing accounts payable can lead to substantial cost savings for your business. Companies can achieve significant financial benefits by reducing operational expenses and optimizing resource allocation. Here are the key areas where cost savings can be realized:
- Reduction in operational costs: Businesses can lower their day-to-day operational expenses by outsourcing accounts payable. External providers streamline processes and leverage economies of scale, reducing the overall cost of managing accounts payable activities.
- Lower staffing and training expenses: Outsourcing eliminates the need for hiring and training in-house AP specialists. Companies can avoid the costs of recruitment, onboarding, and continuous training, allowing them to allocate these resources more effectively.
- Savings on technology and infrastructure: Managing accounts payable in-house often requires significant investments in technology and infrastructure. Outsourcing partners already have the necessary tools and systems, enabling businesses to save on these expenditures. These savings can then be reinvested in other strategic areas to drive growth and innovation.
Improved Efficiency
Outsourcing accounts payable leads to remarkable improvements in efficiency. Here are the key points that contribute to this enhanced efficiency:
- Streamlined AP Processes: External providers utilize advanced technologies and optimized workflows to handle accounts payable tasks. This streamlining ensures that each step in the AP process, from invoice receipt to payment, is executed with precision and speed.
- Faster Invoice Processing and Payment Cycles: Outsourcing results in quicker turnaround times for invoice processing and payments. External providers use automation and specialized software, reducing manual intervention, speeding up the entire cycle, and ensuring vendors are paid promptly.
- Focus on Core Business Activities: By sending their AP functions to outsourced providers, businesses can reallocate their resources to focus on core activities. This shift allows companies to concentrate on their primary objectives without being bogged down by the intricacies of AP management.
Access to Expertise
Outsourcing accounts payable provides access to a team of professionals with extensive experience in AP management. Here are the key benefits of accessing this expertise:
- Professional Handling of AP Tasks: By outsourcing accounts payable, you ensure that professionals in this field manage your AP tasks. Their expertise ensures that invoices are processed efficiently and accurately.
- Compliance with Regulations and Industry Standards: External providers understand the latest regulations and industry standards. They ensure that your AP processes comply with all relevant laws and guidelines, minimizing the risk of non-compliance penalties and enhancing your company’s reputation.
- Up-to-date Knowledge of Best Practices: AP professionals stay current with the latest best practices in accounts payable management. By leveraging their knowledge, your business can benefit from the most effective and efficient AP processes, improving overall performance.
Enhanced Accuracy
Outsourcing accounts payable significantly enhances the accuracy of financial processes. This improvement can be attributed to several key factors:
- Reduction in errors and discrepancies: Outsourcing to professionals who utilize advanced software and processes minimizes the likelihood of manual errors. This precision ensures that all invoices are processed accurately, reducing the risk of discrepancies that can lead to financial misstatements.
- Automated processes and checks: External providers implement automated systems that streamline AP workflows. These systems include built-in checks and balances that catch errors before they occur, maintaining high accuracy levels throughout the AP process.
- Reliable financial reporting: Accurate accounts payable processes provide reliable financial reporting. Outsourcing ensures that financial data is precise and up-to-date, providing a solid foundation for business decision-making and strategic planning.
Scalability
Outsourcing accounts payable offers several advantages when it comes to scalability. Businesses can seamlessly adjust their operations by leveraging external expertise to meet growing and changing demands. Here are the key points of scalability benefits:
- Flexibility to scale operations as the business grows: Outsourcing allows companies to effortlessly expand their accounts payable processes in line with business growth. This means that as your company scales, the AP function can grow with it without the need for significant internal adjustments.
- Handling fluctuations in invoice volumes: Businesses often experience varying invoice volumes due to seasonal trends or market fluctuations. Outsourcing accounts payable ensures that these variations are managed efficiently, with external providers equipped to handle peaks and troughs in demand.
- Adapting to changing business needs: As your business scales, so do its requirements. Outsourcing offers the agility to adapt AP processes to new business models, regulatory changes, and market conditions. This adaptability ensures your AP function remains aligned with overall business strategies and objectives.
Improved Cash Flow Management
Effective cash flow management determines the sustainability and growth of any business. Outsourcing accounts payable offers several advantages that can help optimize your cash flow. Here are the key points:
- Better control over payment schedules: By outsourcing accounts payable, businesses gain precise control over when payments are made. This control helps align payment schedules with cash inflows, ensuring the company maintains a healthy cash flow. Timely payments also help avoid late fees and penalties.
- Optimized working capital: Outsourcing allows for better working capital management by ensuring that funds are allocated efficiently. External providers can analyze payment terms and prioritize invoices based on due dates and cash flow needs, optimizing the use of available funds and preventing cash shortages.
- Enhanced vendor relationships and negotiations: Consistent and timely payments foster strong relationships with vendors. Outsourcing accounts payable enables businesses to negotiate better terms with suppliers. This enhanced relationship can improve service, preferential treatment, and lower costs.
Risk Mitigation
Outsourcing accounts payable significantly mitigates various risks associated with AP processes. By partnering with specialized providers, businesses can benefit from:
- Reduced risk of fraud and compliance issues: External providers implement stringent controls and monitoring systems to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. They stay updated on regulatory changes and ensure that your AP processes comply with the latest standards, minimizing the risk of compliance breaches.
- Implementing robust security measures: Outsourcing partners employ advanced security protocols to safeguard sensitive financial information. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, ensuring your data remains protected against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Comprehensive audit trails and documentation: Detailed records and audit trails maintained by external providers enhance transparency and accountability in AP processes. This thorough documentation is crucial for internal audits, financial reviews, and compliance reporting, providing a clear trail of all transactions and activities.
Outsourcing accounts payable is a strategic move that offers numerous benefits. By leveraging the expertise of outsourced experts, businesses can streamline their AP processes, focus on core activities, and achieve better financial management. Embrace outsourcing accounts payable to unlock these advantages and drive your business toward greater success.
Need help better understanding outsourcing your accounts payable? Contact a NOW CFO specialist for more information.
Get Your Free Consultation
Gain Financial Visibility Into Your Business
We provide outsourced CFO, fractional CFO, and temporary CFO, Controller, and operational Accounting services that suit the needs of your business.
- Hourly Rates
- No Hidden Fees
- No Long Term Requirements
NOW CFO provides the highest level of expertise in finance and operational accounting to accelerate results and achieve strategic objectives for sustainable growth and success.
After completing the form, a NOW CFO Account Executive will reach out and learn more about your needs so that we can pair you with the right Partner.
Learn More: Is It Time to Outsource Your Accounting?
Outsourcing accounting has become an increasingly popular solution for non-profit organizations seeking to manage their financial responsibilities efficiently and effectively. By delegating financial tasks to external experts, non-profits can focus more on their core missions rather than the intricacies of accounting. This approach is particularly beneficial for organizations operating under tight budget constraints or those needing more resources to maintain a full-time accounting department. Outsourcing accounting can offer not just a reduction in costs but also access to a level of expertise that might not otherwise be available internally.
Benefits of Outsourcing Accounting
Outsourcing accounting offers several key advantages:
- Cost Savings: By outsourcing, non-profits can reduce the need for in-house accounting staff, thus saving on salaries, benefits, and training costs. In turn, these resources can be used for project-critical activities.
- Access to Specialized Expertise: Non-profits benefit from the high level of expertise that professional accounting firms offer. These firms stay abreast of the latest practices and regulatory changes, ensuring that knowledgeable professionals handle financial operations.
- Improved Efficiency: With experts handling the financial details, accounting processes become more streamlined and efficient. This leads to faster turnaround times for financial reporting and more accurate financial documents.
- Enhanced Compliance: Professional accountants know the latest financial regulations and reporting standards. Their expertise helps ensure that non-profits comply with these requirements, minimizing the risk of errors and potential financial penalties.
- Increased Financial Accuracy: Outsourcing accounting helps maintain more accurate and up-to-date financial records. Accurate records are crucial for internal decision-making and maintaining the trust of donors and stakeholders.
Identifying the Need for Outsourcing
For non-profit organizations, recognizing the right moment to outsource accounting functions is crucial for maintaining financial health and compliance. Here are key factors that might indicate the need for outsourcing:
- Rapid Growth: When a non-profit grows quickly, its internal resources can be stretched thin, making it challenging to manage increasingly complex financial tasks. Outsourcing accounting can provide the necessary bandwidth and expertise to handle growth efficiently.
- Difficulty in Maintaining Records: If an organization consistently struggles with keeping financial records up-to-date and accurate, it’s a sign that the existing processes need to be revised. Professional accounting services can ensure that financial records are systematically organized and maintained.
- Preparation for Audit: Audits require thorough documentation and precise financial records. If preparing for an audit seems daunting, outsourcing accounting can help ensure that all financial dealings are accurately recorded and compliant with applicable standards, making the audit process smoother and less stressful.
Choosing the Right Accounting Firm
Regarding outsourcing accounting, selecting the right firm is critical for non-profit organizations. Here are several key factors to consider:
- Expertise in Non-Profit Sector: The firm should have a solid track record of working with non-profit organizations. This ensures they understand non-profits’ specific challenges and regulatory environments, such as funding structures, donor reporting, and budget constraints.
- Transparency and Accountability: Choose a firm that values transparency and accountability. The firm should provide clear, comprehensive reporting and open communication channels.
- Scalability: As non-profits grow, their financial needs will evolve. A good accounting firm can scale its services to match your growing needs, whether that involves expanding financial management capabilities or providing additional services.
- Customized Service Offerings: The accounting firm must offer services tailored to your organization’s needs. Customized services ensure that you only pay for what you need, which can be more cost-effective in the long run.
- Integration Capabilities: They must be able to integrate their services with your existing financial systems. This ensures seamless data flow and maintains the integrity of your financial information.
- Strong Communication Protocols: Effective communication is key to any outsourcing relationship. Ensure that your chosen firm has established protocols for regular updates and consultations. Hence, you are always informed and in control of your financial management.
Services Offered by Accounting Firms
Accounting firms provide various essential services tailored to non-profit organizations’ specific needs. Here is a detailed look at each service:
- Bookkeeping: Comprehensive bookkeeping ensures that all financial transactions are meticulously recorded, helping non-profits maintain orderly and accurate records. This service is fundamental for tracking daily financial activities and provides a reliable basis for making strategic decisions.
- Financial Reporting: Detailed financial reports are crucial for non-profits as they assess their financial status, facilitate strategic planning, and ensure transparency. These reports are instrumental in demonstrating accountability to donors, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies, vital for maintaining trust and securing future support.
- Staff Training: For non-profits, comprehensive staff training is essential to ensure that their team is knowledgeable, skilled, and aligned with the organization’s mission and goals. Providing regular training sessions helps staff stay updated on best practices, regulatory requirements, and new technologies. This service enhances the organization’s overall efficiency and effectiveness, fostering a professional and competent workforce capable of achieving the non-profit’s objectives.
- Internal Controls: Robust internal controls are vital for maintaining a non-profit organization’s financial integrity and operational efficiency. Implementing effective internal controls helps to safeguard assets, prevent fraud, and ensure accurate financial reporting. This service provides non-profits with the frameworks and procedures to monitor and manage risks, enhancing accountability and promoting confidence among stakeholders and donors.
Integration with Existing Systems
When non-profit organizations decide to outsource their accounting, integrating these services with their existing financial systems and workflows is crucial for seamless operation. Here are some key points for effective integration:
- Compatibility with Current Systems: Ensure the accounting firm’s software and tools are compatible with your organization’s financial management systems. This compatibility helps in maintaining continuity in financial processes and data integrity.
- Clear Communication Protocols: Establish clear communication channels and protocols between your organization and the accounting firm. This ensures that all financial information is accurately conveyed and that any issues can be promptly addressed.
- Data Sharing Agreements: Set up formal agreements that specify what data will be shared, how it will be protected, and who has access to it. These agreements are essential for protecting sensitive information and ensuring everyone understands their role in handling data.
- Training and Support: Arrange training sessions provided by the accounting firm to familiarize your staff with new systems or changes to existing processes. Ongoing support should also be available to address any issues that arise during the integration phase or regular operations.
Outsourcing accounting is not just a practical financial choice for non-profit organizations; it is a strategic move that can enhance their overall effectiveness and enable them to serve their communities better. By carefully selecting the right firm and integrating their services effectively, non-profits can ensure that their financial management is taken care of, allowing them to focus more on their mission and less on the complexities of accounting.
Need help outsourcing accounting for your non-profit organization? Contact a NOW CFO specialist for more information.
Maintaining robust financial health is crucial in today’s competitive business landscape. However, many small businesses struggle with financial management, leading to significant challenges. Notably, 20% of small businesses fail within the first year, and 50% fail within five years, often due to lacking strategic financial planning.
A financial controller can be instrumental in steering your business toward success. By overseeing financial reporting, ensuring compliance, and aiding in strategic planning, a controller adds substantial value to your operations.
What Is a Financial Controller?
A financial controller serves as a senior-level executive responsible for overseeing an organization’s daily accounting operations and ensuring the accuracy of its financial records. Often referred to as the “company historian,” the controller maintains the integrity of economic data, which is crucial for informed decision-making.
Definition and Core Functions of a Controller
A financial controller acts as the lead accountant within a company, managing comprehensive financial activities to ensure accuracy and compliance. Their core functions include:
- Financial Reporting: Controllers oversee the preparation of financial statements, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. This responsibility ensures stakeholders understand the company’s financial health clearly and accurately.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: They develop and manage budgets and financial forecasts to guide the company’s financial planning and resource allocation. This process involves analyzing historical data and market trends to project future economic performance.
- Internal Controls: Implementing and monitoring internal controls is a key function to safeguard assets, ensure the accuracy of financial records, and prevent fraud. Adequate internal controls are vital for maintaining financial integrity and operational efficiency.
- Compliance Management: Controllers ensure the company adheres to financial regulations and accounting standards, reducing the risk of legal penalties and monetary misstatements. This includes staying updated with changes in laws and regulations that affect financial reporting and practices.
- Supervision of Accounting Staff: They lead and mentor the accounting team, ensuring that all financial transactions are recorded accurately and promptly. This leadership role is crucial for maintaining a competent and efficient accounting department.
Importance of Controllers in Financial Management
Financial controllers play a pivotal role in maintaining an organization’s financial stability and integrity. Their oversight ensures that economic data is accurate, timely, and compliant with regulatory standards, which is essential for strategic planning and operational decision-making.
Moreover, controllers provide critical insights through financial analysis, helping to identify trends, assess risks, and uncover opportunities for cost savings and revenue enhancement. Their expertise supports the organization’s strategic objectives and long-term financial health.
In addition to their traditional roles, financial controllers are increasingly involved in strategic planning and decision support. They collaborate with senior management to develop economic strategies that align with the company’s goals, contributing to informed decision-making and sustainable growth.
Furthermore, controllers’ implementation of robust internal controls helps prevent fraud and financial mismanagement, protecting the company’s assets and reputation. Their vigilance in compliance management ensures adherence to economic regulations, mitigating the risk of legal issues and monetary penalties.
Key Responsibilities of a Financial Controller
Financial controller responsibilities include playing a pivotal role in an organization’s economic health and overseeing various critical functions that ensure accuracy, compliance, and efficiency.

Financial managers and controllers direct organizations’ financial reports. Due to the increasing demand for financial oversight, employment in this sector is expected to grow by 17% from 2021 to 2033.
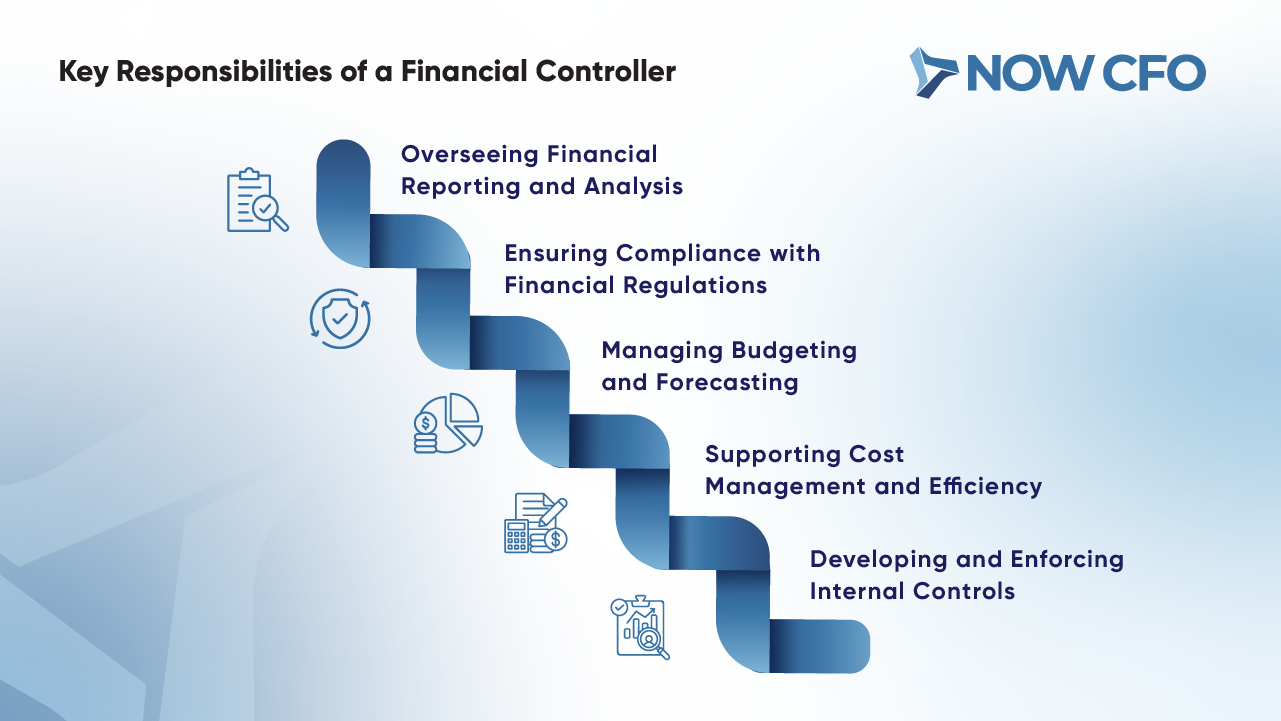
Overseeing Financial Reporting and Analysis
Financial reporting and analysis lie at the core of a financial controller’s role. They generate key financial statements, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow reports. These documents serve as critical tools for understanding a company’s economic performance.
- Data Consolidation and Accuracy: Controllers collect, consolidate, and ensure the accuracy of financial data, which helps build reliable reports.
- Stakeholder Communication: Reports generated by controllers provide stakeholders, such as investors and executives, with essential insights for informed decision-making.
Moreover, financial analysis extends beyond basic reporting. Controllers identify trends and patterns within the data, offering recommendations for revenue growth and cost management.
Ensuring Compliance with Financial Regulations
Another critical duty of controllers is ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Financial regulations evolve frequently, making it imperative for organizations to stay updated.
- Adhering to Standards: Controllers enforce compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), ensuring reports meet global standards.
- Monitoring Regulatory Updates: Controllers help mitigate risks by staying informed about changes in tax laws, audit rules, and other financial regulations.
- Collaboration with Auditors: Controllers often liaise with internal and external auditors to address discrepancies and ensure transparency.
Failure to comply with financial regulations can result in penalties and reputational damage. Controllers play a vital role in preventing these outcomes.
Managing Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting are integral to financial planning and organizational success. Controllers oversee these activities to align resources with the company’s strategic goals.
- Budget Development: Collaborating with department heads and controllers to draft budgets that allocate funds effectively.
- Forecasting Future Performance: Controllers utilize historical data and market trends to create financial forecasts that predict revenue, expenses, and cash flow.
- Scenario Planning: They prepare contingency plans to address potential financial challenges, ensuring the organization remains resilient.
Supporting Cost Management and Efficiency
Cost management directly impacts an organization’s bottom line, and controllers are instrumental in optimizing efficiency. Their responsibilities include:
- Expense Monitoring: Controllers track and analyze department spending to identify waste areas.
- Cost-Saving Initiatives: By evaluating operations, they recommend strategies to minimize unnecessary expenses, such as renegotiating supplier contracts or adopting technological solutions.
- Performance Metrics: They establish KPIs to assess operational efficiency and align spending with business objectives.
Developing and Enforcing Internal Controls
Internal controls are fundamental to safeguarding an organization’s financial integrity. Controllers design and implement these mechanisms to prevent errors, fraud, and economic mismanagement.
- Risk Mitigation: Controllers identify areas of vulnerability within financial processes and establish safeguards.
- Policy Enforcement: They maintain operational consistency by enforcing explicit approvals, documentation, and reconciliations protocols.
- Periodic Audits: Regular internal audits conducted by controllers ensure compliance with established controls.
The Role of a Controller vs. CFO: Key Differences
Although “controller” and “CFO” are often used interchangeably, their roles differ significantly in focus and scope. Understanding these distinctions can help businesses allocate their financial leadership effectively.
Focus Areas and Responsibilities
Financial controller responsibilities include focusing on the internal workings of business financial management, while a CFO takes on a broader, strategic role.
Controller Responsibilities:
- Overseeing accounting functions, including financial reporting and compliance.
- Ensuring accurate financial records through audits and internal controls.
- Managing day-to-day financial operations, such as payroll and budgeting.
CFO Responsibilities:
- Developing financial strategies aligned with the company’s goals.
- Building relationships with investors and stakeholders to secure funding.
- Driving high-level decision-making related to mergers, acquisitions, and long-term growth.
Controllers ensure the financial engine runs smoothly, while CFOs chart the course for the organization’s economic future.
Strategic vs. Operational Financial Leadership
Controllers and CFOs play complementary roles, each emphasizing different aspects of financial management.
- Controllers: Primarily operational, they focus on the present. Their work revolves around maintaining financial integrity, optimizing processes, and ensuring regulatory financial compliance.
- CFOs: Highly strategic, they concentrate on the future. CFOs analyze market conditions, identify growth opportunities, and craft financial plans for long-term success.
Key Example: While a controller might prepare detailed cost analyses for current operations, a CFO would use that data to decide whether expanding into a new market is financially viable.
How Controllers and CFOs Collaborate
The synergy between controllers and CFOs is vital for effective business financial management.
- Data Sharing: Controllers provide CFOs with accurate financial data, enabling them to make informed strategic decisions.
- Compliance Support: Controllers ensure adherence to financial regulations, freeing CFOs to focus on big-picture planning.
- Joint Problem-Solving: Both roles collaborate on resolving financial challenges, such as improving cash flow or securing investment.
Example: During a merger, a controller ensures financial compliance with reporting requirements while the CFO negotiates terms and aligns the merger with the company’s strategic objectives.
How a Controller Adds Value to Your Business
A financial controller significantly influences a business’s success by ensuring effective financial management. Their work enhances transparency, drives efficiency, supports decision-making, and fosters growth. Here’s a detailed look at how they achieve these results.
Enhancing Financial Transparency and Accuracy
Controllers play a pivotal role in ensuring financial transparency. Accurate and transparent financial records give stakeholders a complete picture of the company’s financial health.
- Data Validation: Controllers meticulously verify data, ensuring that financial reports are error-free and reliable.
- Standardized Reporting: They implement uniform reporting standards to maintain consistency, making financial statements more straightforward to understand for both internal teams and external stakeholders.
- Compliance Assurance: Controllers enhance trust and credibility by adhering to accounting standards such as GAAP or IFRS.
Improving Operational Efficiency
Efficient financial operations can significantly enhance a company’s overall performance, and controllers excel in streamlining processes. Businesses that invest in financial process automation see up to a 70% increase in efficiency within two years.
- Automation of Routine Tasks: Controllers identify opportunities to automate repetitive accounting processes, such as payroll and invoicing. This reduces manual errors and saves time.
- Optimized Workflows: They assess existing workflows to identify inefficiencies and recommend adjustments, ensuring optimal resource allocation.
- Cost Reduction: By monitoring expenses closely, controllers help identify unnecessary costs and implement effective cost-saving measures.
Supporting Data-Driven Decision Making
A controller provides valuable insights that support informed decision-making. They analyze financial data to help leaders make strategic choices.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Controllers identify trends and patterns from historical data, offering actionable insights for future planning.
- Forecasting Tools: Advanced forecasting methods equip businesses to anticipate financial challenges and opportunities.
- Performance Metrics: Controllers develop key performance indicators (KPIs) tailored to the company’s goals, helping leaders monitor and adjust strategies.
Helping with Strategic Planning and Growth
Strategic planning requires a deep understanding of financial health, which controllers are uniquely positioned to provide.
- Growth Strategies: Controllers collaborate with executives to create financial strategies that support expansion, whether through investments, mergers, or acquisitions.
- Long-Term Planning: They assist in developing financial roadmaps that align with the company’s mission and goals.
- Risk Management: Controllers help identify financial risks and prepare mitigation strategies to safeguard long-term success.
When Should Your Business Consider Hiring a Controller?
Timing is crucial in deciding when to hire a financial controller. Understanding key signs and the associated benefits helps businesses make informed decisions about expanding their business financial management capabilities.
Signs Your Company Needs a Financial Controller
Recognizing the need for a controller often comes down to observing challenges in financial management.
- Inconsistent Financial Records: If your books frequently show discrepancies, it indicates a need for professional oversight.
- Complex Business Operations: Growing businesses often deal with intricate financial processes, making a controller essential to manage compliance, reporting, and cash flow.
- Leadership Time Constraints: A controller can take over day-to-day financial operations when CFOs or business owners spend too much time on accounting tasks instead of strategic planning.
Benefits for Small to Mid-Sized Businesses
Hiring a controller is often perceived as a resource reserved for large corporations, but small to mid-sized businesses can benefit significantly:
- Scalability: Controllers create financial systems that scale with growth, preparing businesses for expansion.
- Risk Mitigation: They implement strong internal controls, reducing the risk of fraud and mismanagement.
- Improved Decision-Making: With accurate financial data, controllers provide insights that empower leaders to make informed strategic decisions.
Controllers bridge the gap between day-to-day accounting and high-level financial strategy, enabling smaller businesses to operate like larger competitors.
Cost Considerations for Hiring a Controller
While the cost of hiring a controller may seem high initially, the long-term value they bring justifies the investment.
- Full-Time vs. Fractional Controllers: Businesses can choose between full-time controllers, which are ideal for large operations, and fractional controllers, which are more cost-effective for smaller businesses.
- Cost Offsets: Controllers help identify inefficiencies and reduce financial risks, often saving more than their salary in operational improvements and risk mitigation.
How to Choose the Right Controller for Your Business
Selecting the right financial controller is a critical decision that impacts your company’s financial health. By evaluating their skills, experience, and cultural fit, businesses can ensure they hire a candidate who aligns with their goals.
Key Skills and Qualifications to Look For
When hiring a controller, focus on their technical proficiency and leadership abilities.
- Accounting Expertise: Ensure candidates understand accounting principles, including GAAP or IFRS.
- Analytical Skills: Controllers must analyze financial data effectively to identify trends and provide actionable insights.
- Communication Abilities: Look for someone who can clearly explain financial concepts to non-financial stakeholders.
- Certifications: Credentials like CPA (Certified Public Accountant) or CMA (Certified Management Accountant) are indicators of expertise and dedication to the profession.
Industry Experience and Technical Expertise
A controller with relevant industry experience can quickly adapt to your business needs.
- Specialized Knowledge: Someone who understands the nuances of your industry can identify sector-specific challenges and opportunities. For instance, a controller familiar with retail might excel in managing inventory and supply chain costs.
- Technology Proficiency: Expertise in financial software such as QuickBooks, NetSuite, or ERP systems is essential for efficient operations.
Evaluating Cultural Fit and Leadership Skills
A controller must align with your organization’s culture and demonstrate strong leadership.
- Adaptability: Ensure the candidate can thrive in your company’s fast-paced or traditional environment.
- Team Leadership: Controllers often manage accounting teams, so they must inspire collaboration and efficiency.
- Problem-Solving Mindset: Look for candidates who can resolve financial challenges with innovative solutions.
Questions to Ask in the Hiring Process
Asking the right questions during interviews can help assess a controller’s suitability:
- How do you ensure accuracy and compliance in financial reporting?
- Can you share an example of a cost-saving initiative you implemented?
- What strategies do you use to manage a team under tight deadlines?
- Which financial software are you most proficient in?
- How have you handled regulatory challenges in past roles?
Conclusion: Maximizing Business Success with a Controller
Investing in a financial controller is a strategic move that can significantly enhance your company’s economic stability and growth prospects. The active role of a controller ensures accurate financial management and provides insights that drive informed decision-making.
If you’re ready to strengthen your financial foundation and propel your business forward, consider consulting with our team of experienced controllers. Contact NOW CFO, schedule a consultation, and discover how we can tailor our services to meet your business needs.
The role of your staff accountant is important in your business. These professionals form the backbone of an organization’s financial operations, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and strategic financial planning. A well-qualified staff accountant can significantly influence your business’s financial health and sustainability as a record keeper and a key decision-maker in financial matters.
Staff Accountant Essential Qualifications
Choosing the right staff accountant for your organization involves careful consideration of their educational background and certifications:
- Bachelor’s Degree in Accounting: This essential qualification equips an accountant with the fundamental accounting principles and practices to effectively handle your organization’s financial responsibilities.
- Certifications such as CPA: A Certified Public Accountant (CPA) license is highly respected. Maintaining the license requires a rigorous exam and fulfilling continuing education requirements. This certification is crucial as it indicates a high level of expertise and a commitment to ethical standards.
- Ongoing Education: The accounting landscape continually evolves with new laws, technologies, and methodologies. Ongoing education is vital for a staff accountant to stay current and effective, ensuring they can handle complex financial scenarios and regulatory changes.
- Advanced Degrees or Certifications (CMA, MBA): Pursuing an advanced degree or obtaining certifications like a Certified Management Accountant (CMA) can greatly enhance an accountant’s knowledge and strategic thinking abilities. These qualifications enable them to contribute more significantly to financial analysis, decision-making, and strategic planning at a higher level within your organization.
Core Staff Accounting Skills
Your staff accountant should possess a comprehensive skill set that ensures accuracy and compliance with financial laws and practices. Key skills include:
- Proficiency in Accounting Principles and Practices: Mastery of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), knowledge of tax laws, and expertise in financial reporting are essential. These skills ensure that all financial activities are conducted according to legal and professional standards, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your financial statements.
- Management of Financial Transactions: This involves handling accounts payable and receivable, managing the general ledger, overseeing payroll operations, and ensuring accurate tax documentation. Your staff accountant should streamline these processes to enhance financial efficiency and accuracy.
- Attention to Detail and Accuracy: In financial reporting, precision is paramount. Your staff accountant must be meticulous to ensure that every financial statement and report is error-free. This accuracy builds trust and reliability in your financial data, which is crucial for decision-making at all levels of the organization.
Technological Proficiency
Technological proficiency is crucial for modern accounting roles, and your staff accountant should be adept with various digital tools. Here are the key technological competencies they should possess:
- Accounting Software: Proficiency in QuickBooks, Microsoft Dynamics, or SAP software is essential. These systems help manage financial transactions, generate reports, and ensure compliance with financial regulations.
- Excel and Data Analysis Tools: Mastery of Excel is critical for handling complex datasets, performing financial analysis, and creating detailed reports. Knowledge of other data analysis tools can also enhance their ability to interpret financial data effectively.
- Automation and Data Analytics: Understanding the role of automation and data analytics in accounting can significantly increase efficiency and accuracy. Your staff accountant should be familiar with how these technologies can be applied to streamline operations and provide deeper insights into financial trends.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving skills are skills your staff accountant should possess. These skills ensure they can effectively navigate complex financial landscapes:
- Analyzing Financial Data: Your staff accountant should excel at dissecting financial data to unearth underlying patterns and anomalies. This skill is crucial for identifying discrepancies and potential issues and spotting cost savings and investment opportunities. They should be capable of transforming raw data into actionable insights that can influence decision-making and strategic planning.
- Solving Common Financial Problems: From reconciling budget discrepancies to optimizing cash flow and managing financial risks, your staff accountant must be adept at solving routine and unforeseen financial problems. These challenges require a proactive approach and creative thinking to ensure the financial operations remain smooth and efficient, ultimately supporting the business’s overall stability.
- Strategic Financial Decision-Making: Strategic thinking is vital beyond day-to-day problem-solving. It allows your staff accountant to contribute to broader business strategies, ensuring that financial plans align with long-term business goals. They should be involved in formulating financial policies and plans that support the company’s growth initiatives, ensuring that every financial decision is made with a clear understanding of its impact on the future.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
Effective communication and robust interpersonal skills are indispensable attributes for your staff accountant. These skills ensure smooth interactions and clearer financial understanding across all levels of the organization:
- Articulating Financial Data: Your staff accountant must be adept at conveying complex financial data clearly and concisely. This involves preparing detailed reports and translating these figures into layperson’s terms during presentations or meetings. Their ability to demystify financial jargon helps stakeholders from various departments make well-informed decisions that align with the organization’s goals.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: The role of your staff accountant often intersects with various parts of the organization, from budgeting teams to external auditors. Their ability to effectively collaborate and integrate their expertise with other team members is crucial for the timely and successful completion of projects. This teamwork fosters a more cohesive work environment, providing more accurate and holistic financial outcomes.
- Interacting with Stakeholders: Regular interactions with diverse stakeholders are key to a staff accountant’s duties. They must maintain clarity, confidence, and professionalism, explaining budget variances to management, advising on the financial implications of strategic decisions, or negotiating with suppliers. Effective communication in these interactions helps build trust and ensure transparency, which is critical for maintaining long-term relationships and upholding the company’s reputation.
Ethics and Integrity
Ethical standards are non-negotiable in accounting. Your staff accountant plays a critical role in maintaining these standards, which include:
- Upholding Integrity and Professionalism: Your staff accountant must conduct all financial activities honestly and honestly. This means adhering strictly to accounting laws and regulations to avoid legal issues.
- Promoting Transparency: Transparency in financial reporting is crucial. It ensures compliance with financial regulations and builds trust among stakeholders. Your staff accountant should ensure that all financial information is accurate and readily accessible to authorized parties.
- Consequences of Ethical Breaches: Ethical breaches can lead to severe consequences for your business, including legal penalties, loss of reputation, and financial harm. It is imperative that your staff accountant understands the implications of unethical behavior and works diligently to avoid such pitfalls.
Your staff accountant’s contributions are vital to your organization’s operational success and financial stability. By ensuring they possess the right qualifications, skills, and ethical standards, you secure a functional employee and a strategic partner in your business’s growth. Your staff accountant is more than a number cruncher; they are a pivotal part of your team’s success and your company’s future.
Need help finding a staff accountant for your business? Contact a NOW CFO specialist for more information.
Learn More: The Role of a Controller in Your Business
In any organization, the role of an accounting manager is pivotal in steering the company toward its financial goals. As the backbone of financial management and organizational strategy, the importance of the accounting manager cannot be overstated. These professionals ensure that all financial dealings are accurately recorded and strategize on fiscal management to propel the organization forward.
Core Responsibilities Of An Accounting Manager
The role of an accounting manager is complex and multifaceted, encompassing a range of critical responsibilities that ensure an organization’s financial health and operational efficiency. From detailed financial reporting to strategic budget management and rigorous compliance oversight, here’s a closer look at the core responsibilities that define the success and leadership of an accounting manager:
- Financial Analysis and Reporting: An accounting manager is responsible for preparing, accurately, and timely delivering financial reports. These reports include balance sheets, income, and cash flow statements critical for internal and external stakeholders. By ensuring that these documents comply with legal and regulatory standards, such as GAAP or IFRS, the accounting manager safeguards the organization against financial misreporting and fraud. Furthermore, they make complex financial data accessible and understandable to non-financial stakeholders, aiding in strategic decision-making and enhancing transparency across the organization.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Budgeting and forecasting has the accounting manager leading the annual budgeting process by setting financial targets and allocating resources efficiently across departments. This process involves collaboration with department heads to ensure that their financial needs are met and that their spending aligns with corporate objectives. Forecasting, another pivotal responsibility, requires the accounting manager to analyze past financial data and predict future trends. This foresight helps prepare the organization for future challenges and opportunities, making it possible to adjust financial strategies dynamically to maintain financial health and competitive advantage.
- Cash Management: Effective cash management is crucial for the survival and growth of any organization, and the accounting manager plays a central role in this area. They ensure that the organization has enough liquidity to meet its obligations and opt for investment opportunities that could yield significant returns. This includes managing operational cash flows, optimizing the company’s investment portfolio, and devising strategies for effective debt management. By maintaining a robust cash management system, the accounting manager helps the organization minimize financial risk and maximize investment returns.
- Audit and Compliance: Accounting managers are key liaisons between the company and external auditors during financial audits. They ensure that all financial statements and practices undergo scrutiny to uphold transparency and compliance with laws and regulations. Post-audit, they are responsible for addressing any discrepancies or recommendations from the audit, which may involve refining financial policies or introducing new controls. Moreover, by fostering a culture of compliance and ethical behavior within the finance department, the accounting manager reinforces the integrity of the financial management system.
- Team Leadership and Development: As finance team leaders, accounting managers are responsible for more than just overseeing tasks; they are also mentors and role models for their staff. This involves recruiting skilled financial professionals, providing ongoing training, and promoting career development to enhance team capabilities. By encouraging a culture of innovation, ethical practices, and continuous improvement, accounting managers ensure that their teams are adaptable and highly competent. Their leadership is instrumental in building a cohesive team that is proactive in facing new financial challenges.
Technology and Innovation
Cutting-edge technologies not only enhance operational efficiencies but also provide critical strategic advantages. Here’s how modern accounting managers are integrating technology into their daily operations to remain competitive and effective:
- Implement and Manage Accounting Software and Systems: Accounting managers are tasked with implementing and managing sophisticated accounting software and systems. These tools are crucial for automating standard tasks, reducing the likelihood of human error, and providing real-time financial insights. By leveraging advanced software solutions, accounting managers can streamline workflows, enhance data integrity, and improve overall financial reporting efficiency.
- Stay Updated on Technological Advancements: To maintain a competitive edge, it is vital for accounting managers to keep abreast of technological advancements in the field of finance. This includes exploring emerging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning that can profoundly impact financial processes and reporting. By staying informed, accounting managers can anticipate changes and adapt strategies that align with technological evolution.
- Streamline Accounting Processes and Improve Accuracy: Streamlining technologies helps refine and optimize accounting processes. This speeds up operations and increases the accuracy and reliability of financial data. For example, using AI for data analysis can help identify trends and anomalies faster than traditional methods, enabling proactive financial management. Additionally, technology is pivotal in ensuring that financial data is consistent and error-free, which is essential for making informed business decisions.
Strategic Involvement
The strategic involvement of accounting managers ensures that financial considerations are seamlessly integrated with corporate decision-making, enabling informed and effective strategies that drive growth and sustainability. Here’s how accounting managers contribute to and influence key strategic areas within the organization:
- Participate in Strategic Planning and Decision-Making Processes: Accounting managers are integral participants in strategic planning sessions, providing financial analyses crucial for shaping the organization’s long-term goals. Their insights help assess the viability of proposed projects and strategies financially, ensuring that the decisions are financially sound and aligned with the organization’s capacity and objectives.
- Provide Financial Insights and Analysis to Support Corporate Strategy and Growth Initiatives: An accounting manager plays a vital role in supporting corporate strategies and growth initiatives by offering detailed financial insights. These insights include profitability analysis, cost identification and allocation, and investment appraisal. The accounting manager helps guide the organization toward profitable and sustainable growth by understanding financial metrics and trends.
- Emphasize How Accounting Managers Can Influence Organizational Direction Through Financial Leadership: The leadership role of an accounting manager extends beyond numbers; it is about influencing the broader organizational direction. By acting as a bridge between the financial health of the company and its strategic objectives, accounting managers ensure that financial strategies reflect and contribute to the broader business goals. Their strategic involvement makes them pivotal in steering the organization toward achieving its overarching visions and objectives.
The role of an accounting manager is indispensable in today’s business environment. From managing complex financial operations to driving strategic decisions, the effectiveness of an accounting manager is a significant determinant of an organization’s success.
Do you need help finding an accounting manager? Contact a NOW CFO specialist for more information.
Learn More: Is It Time to Outsource Your Accounting?